Use of conditioned media (CM) and xeno-free serum substitute on human adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) differentiation into urothelial-like cells
- PMID: 33850639
- PMCID: PMC8019311
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.10890
Use of conditioned media (CM) and xeno-free serum substitute on human adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) differentiation into urothelial-like cells
Abstract
Background: Congenital abnormalities, cancers as well as injuries can cause irreversible damage to the urinary tract, which eventually requires tissue reconstruction. Smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and urothelial cells are the major cell types required for the reconstruction of lower urinary tract. Adult stem cells represent an accessible source of unlimited repertoire of untransformed cells.
Aim: Fetal bovine serum (FBS) is the most vital supplement in the culture media used for cellular proliferation and differentiation. However, due to the increasing interest in manufacturing xeno-free stem cell-based cellular products, optimizing the composition of the culture media and the serum-type used is of paramount importance. In this study, the effects of FBS and pooled human platelet (pHPL) lysate were assessed on the capacity of human adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) to differentiate into urothelial-like cells. Also, we aimed to compare the ability of both conditioned media (CM) and unconditioned urothelial cell media (UCM) to induce urothelial differentiation of ADCS in vitro.
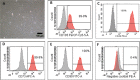
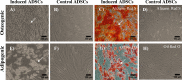
Methods: ADSCs were isolated from human lipoaspirates and characterized by flow cytometry for their ability to express the most common mesenchymal stem cell (MSCs) markers. The differentiation potential was also assessed by differentiating them into osteogenic and adipogenic cell lineages. To evaluate the capacity of ADSCs to differentiate towards the urothelial-like lineage, cells were cultured with either CM or UCM, supplemented with either 5% pHPL, 2.5% pHPL or 10% FBS. After 14 days of induction, cells were utilized for gene expression and immunofluorescence analysis.
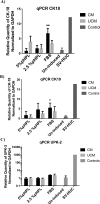
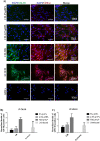
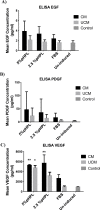
Results: ADSCs cultured in CM and supplemented with FBS exhibited the highest upregulation levels of the urothelial cell markers; cytokeratin-18 (CK-18), cytokeratin-19 (CK-19), and Uroplakin-2 (UPK-2), with a 6.7, 4.2- and a 2-folds increase in gene expression, respectively. Meanwhile, the use of CM supplemented with either 5% pHPL or 2.5% pHPL, and UCM supplemented with either 5% pHPL or 2.5% pHPL showed low expression levels of CK-18 and CK-19 and no upregulation of UPK-2 level was observed. In contrast, the use of UCM with FBS has increased the levels of CK-18 and CK-19, however to a lesser extent compared to CM. At the cellular level, CK-18 and UPK-2 were only detected in CM/FBS supplemented group. Growth factor analysis revealed an increase in the expression levels of EGF, VEGF and PDGF in all of the differentiated groups.
Conclusion: Efficient ADSCs urothelial differentiation is dependent on the use of conditioned media. The presence of high concentrations of proliferation-inducing growth factors present in the pHPL reduces the efficiency of ADSCs differentiation towards the urothelial lineage. Additionally, the increase in EGF, VEGF and PDGF during the differentiation implicates them in the mechanism of urothelial cell differentiation.
Keywords: Adipose stem cells; Cellular differentiation; Pooled human platelet lysate; Urothelial cells.
©2021 Alkurdi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of mitotic bookmarking factors during enhanced proliferation of human stromal cells in human platelet lysate.J Transl Med. 2019 Dec 30;17(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-02183-0. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31888679 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of medium supplementation and serial passaging on the transcriptome of human adipose-derived stromal cells expanded in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Aug 14;10(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1370-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31412930 Free PMC article.
-
Pooled human platelet lysate versus fetal bovine serum-investigating the proliferation rate, chromosome stability and angiogenic potential of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells intended for clinical use.Cytotherapy. 2013 Sep;15(9):1086-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.01.217. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cytotherapy. 2013. PMID: 23602579
-
Influences of Xeno-Free Media on Mesenchymal Stem Cell Expansion for Clinical Application.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021 Feb;18(1):15-23. doi: 10.1007/s13770-020-00306-z. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021. PMID: 33150562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose stem cells in tissue regeneration and repair: From bench to bedside.Regen Ther. 2023 Oct 11;24:547-560. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2023.09.014. eCollection 2023 Dec. Regen Ther. 2023. PMID: 37854632 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kartogenin Induced Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes Enhance the Chondrogenic Differentiation Ability of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells.Dis Markers. 2022 Aug 29;2022:6943630. doi: 10.1155/2022/6943630. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36072901 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of stem cells and cell products involved in trauma injury.Regen Ther. 2025 Mar 11;29:60-76. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.02.011. eCollection 2025 Jun. Regen Ther. 2025. PMID: 40143930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of hypoxia on proliferation and differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 2;10(19):e38857. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38857. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39421364 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cigarette smoke on the proliferation, viability, gene expression, and cellular functions of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from smoking and non-smoking donors.Biol Open. 2024 Dec 15;13(12):bio061665. doi: 10.1242/bio.061665. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 39625294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aliaghaei A, Gardaneh M, Maghsoudi N, Salehinejad P, Gharib E. Dopaminergic induction of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells by conditioned medium of choroid plexus epithelial cells reduces apomorphine-induced rotation in parkinsonian rats. Archive of Iranian Medecine. 2016;19(8):561–570. - PubMed
-
- Alves da Silva ML, Costa-Pinto AR, Martins A, Correlo VM, Sol P, Bhattacharya M, Faria S, Reis RL, Neves NM. Conditioned medium as a strategy for human stem cells chondrogenic differentiation. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. 2015;9(6):714–723. doi: 10.1002/term.1812. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

