Protocolized ventilator weaning verses usual care: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 33850830
- PMCID: PMC8033208
- DOI: 10.4103/IJCIIS.IJCIIS_29_20
Protocolized ventilator weaning verses usual care: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Protocolized ventilator weaning (PW) strategies utilizing spontaneous breathing trials (SBTs) result in shorter intubation duration and intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay (LOS). We compared respiratory therapy (RT)-driven PW versus usual care (UC) as it pertains to physiologic respiratory parameters, intubation duration, extubation success/reintubation rates, and ICU LOS.
Methods: prospective, multicentric, randomized controlled trial was performed in closed medical and surgical ICUs with 24/7 in-house intensivist coverage at six academic medical centers in a resource-limited setting from October 18, 2007, to May 03, 2014. Extubation readiness was determined by the attending physician (UC) or the respiratory therapist (PW) using predefined criteria and SBT. Physiologic variables, serial blood gas measurements, and weaning indices were assessed including the Rapid Shallow Breathing Index (RSBI), negative inspiratory force (NIF), occlusion pressure (P0.1), and dynamic and static compliance (Cdyn and Cs).
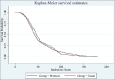
Results: total of 5502 patients were randomized (PW 2787; UC 2715), of which 167 patients died without ventilator weaning (PW 90; UC 77) and 645 patients were excluded (PW 365; UC 280). Finally, a total of 4200 patients were analyzed (PW 2075; UC 2125). The PW group displayed improvements in minute ventilation (P < 0.001), Cs and Cdyn(both P < 0.05), P0.1 (P < 0.001), NIF (P < 0.001), and RSBI (P < 0.001). Early re-intubation (≤48 h) rates were lower in the PW group (16.7% vs. 24.8%; P < 0.0001), as were late re-intubation rates (5.2% vs. 25.8%; P < 0.0001). Intubation duration was longer in the PW group (P < 0.001), however, hospital LOS was shorter (P < 0.001). Mortality was unchanged (P = 0.19).
Conclusion: PW with RT-driven extubation decisions is safe, effective, and associated with decreased re-intubation (early and late), shorter hospital stays, increased intubation duration (statistically but not clinically significant), and unchanged in-patient mortality.
Keywords: Airway extubation; critical care; respiration artificial; respiratory insufficiency; ventilator weaning.
Copyright: © 2020 International Journal of Critical Illness and Injury Science.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Esteban A, Frutos F, Tobin MJ, Alía I, Solsona JF, Valverdú I, et al. A comparison of four methods of weaning patients from mechanical ventilation. Spanish Lung Failure Collaborative Group. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:345–50. - PubMed
-
- MacIntyre NR, Cook DJ, Ely EW, Jr, Epstein SK, Fink JB, Heffner JE, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for weaning and discontinuing ventilatory support: A collective task force facilitated by the American College of Chest Physicians; the American Association for Respiratory Care; and the American College of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 2001;120:375S–95S. - PubMed
-
- Jones DP, Byrne P, Morgan C, Fraser I, Hyland R. Positive end-expiratory pressure vs. T-piece. Extubation after mechanical ventilation. Chest. 1991;100:1655–9. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrini JA, Moraes RB, Maccari JG, de Oliveira RP, Savi A, Ribeiro RA, et al. Spontaneous breathing trials with T-Piece or pressure support ventilation. Respir Care. 2016;61:1693–703. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources