This is a preprint.
Glucocorticoids and B Cell Depleting Agents Substantially Impair Immunogenicity of mRNA Vaccines to SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33851176
- PMCID: PMC8043473
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.04.05.21254656
Glucocorticoids and B Cell Depleting Agents Substantially Impair Immunogenicity of mRNA Vaccines to SARS-CoV-2
Update in
-
Effect of Immunosuppression on the Immunogenicity of mRNA Vaccines to SARS-CoV-2 : A Prospective Cohort Study.Ann Intern Med. 2021 Nov;174(11):1572-1585. doi: 10.7326/M21-1757. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Ann Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34461029 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases (CID) are frequently treated with immunosuppressive medications that can increase their risk of severe COVID-19. While novel mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccination platforms provide robust protection in immunocompetent individuals, the immunogenicity in CID patients on immunosuppression is not well established. Therefore, determining the effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in the setting of immunosuppression is essential to risk-stratify CID patients with impaired protection and provide clinical guidance regarding medication management.
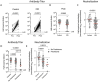
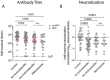
Methods: We conducted a prospective assessment of mRNA-based vaccine immunogenicity in 133 adults with CIDs and 53 immunocompetent controls. Blood from participants over 18 years of age was collected before initial immunization and 1-2 weeks after the second immunization. Serum anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) IgG + binding, neutralizing antibody titers, and circulating S-specific plasmablasts were quantified to assess the magnitude and quality of the humoral response following vaccination.
Results: Compared to immunocompetent controls, a three-fold reduction in anti-S IgG titers (P=0.009) and SARS-CoV-2 neutralization (p<0.0001) were observed in CID patients. B cell depletion and glucocorticoids exerted the strongest effect with a 36- and 10-fold reduction in humoral responses, respectively (p<0.0001). Janus kinase inhibitors and antimetabolites, including methotrexate, also blunted antibody titers in multivariate regression analysis (P<0.0001, P=0.0023, respectively). Other targeted therapies, such as TNF inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors, and integrin inhibitors, had only modest impacts on antibody formation and neutralization.
Conclusions: CID patients treated with immunosuppressive therapies exhibit impaired SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-induced immunity, with glucocorticoids and B cell depletion therapy more severely impeding optimal responses.
Figures

References
-
- Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr., et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:1–26. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
