The Evolution and Distribution of Pneumococcal Serotypes in Adults Hospitalized With Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Spain Using a Serotype-Specific Urinary Antigen Detection Test: The CAPA Study, 2011-2018
- PMID: 33851220
- PMCID: PMC8442776
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciab307
The Evolution and Distribution of Pneumococcal Serotypes in Adults Hospitalized With Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Spain Using a Serotype-Specific Urinary Antigen Detection Test: The CAPA Study, 2011-2018
Abstract
Background: Spain introduced the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) in the childhood National Immunization Program in 2015-2016 with coverage of 3 doses of 94.8% in 2018. We assessed the evolution of all pneumococcal, PCV13 vaccine type (VT), and experimental PCV20-VT (PCV13 + serotypes 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 22F, 33F) hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in adults in Spain from 2011-2018.
Methods: A prospective observational study of immunocompetent adults (≥18 years) admitted to 4 Spanish hospitals with chest X-ray-confirmed CAP between November 2011 and November 2018. Microbiological confirmation was obtained using the Pfizer serotype-specific urinary antigen detection tests (UAD1/UAD2), BinaxNow test for urine, and conventional cultures of blood, pleural fluid, and high-quality sputum.
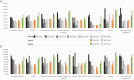
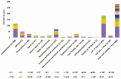
Results: Of 3107 adults hospitalized with CAP, 1943 were ≥65 years. Underlying conditions were present in 87% (n = 2704) of the participants. Among all patients, 895 (28.8%) had pneumococcal CAP and 439 (14.1%) had PCV13-VT CAP, decreasing from 17.9% (n = 77) to 13.2% (n = 68) from 2011-2012 to 2017-2018 (P = .049). PCV20-VT CAP occurred in 243 (23.8%) of those included in 2016-2018. The most identified serotypes were 3 and 8. Serotype 3 accounted for 6.9% (n = 215) of CAP cases, remaining stable during the study period, and was associated with disease severity.
Conclusions: PCV13-VT caused a substantial proportion of CAP in Spanish immunocompetent adults 8 years after introduction of childhood PCV13 immunization. Improving direct PCV13 coverage of targeted adult populations could further reduce PCV13-VT burden, a benefit that could be increased further if PCV20 is licensed and implemented.
Keywords: PCV13 serotypes; community-acquired pneumonia; pneumococcal conjugate vaccines; pneumococcal pneumonia.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
Comment in
-
What Fraction of Adult Community-Acquired Pneumonia Is Caused by the Pneumococcus? New Insights from Spain.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 15;73(6):1086-1088. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab314. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33851210 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- G. B. D. Lower Respiratory Infections Collaborators. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory infections in 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18:1191–210. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feldman C, Anderson R. The role of streptococcus pneumoniae in community-acquired pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2016; 37:806–18. - PubMed
-
- Pilishvili T, Lexau C, Farley MM, et al. ; Active Bacterial Core Surveillance/Emerging Infections Program Network . Sustained reductions in invasive pneumococcal disease in the era of conjugate vaccine. J Infect Dis 2010; 201:32–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

