The cumulative incidence of dysphagia and dysphagia-free survival in persons diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 33851421
- PMCID: PMC8217360
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.27244
The cumulative incidence of dysphagia and dysphagia-free survival in persons diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
Introduction/aims: Dysphagia worsens mortality and quality of life for persons diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), yet our understanding of its incidence and timing remains limited. In this study we sought to estimate dysphagia incidence and dysphagia-free survival over time.
Methods: Using data from the Pooled Resource Open-Access ALS Clinical Trials Database, we compared characteristics of persons with and without dysphagia upon study entry. To account for competing mortality risk, we used Kaplan-Meier curves to estimate the cumulative incidence of dysphagia and the median number of days until the development of dysphagia or death in those without dysphagia at study entry.
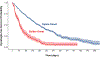
Results: Patients with dysphagia upon study entry were more likely to have bulbar onset and had faster rates of functional decline and shorter diagnostic delays. The cumulative incidence of new-onset dysphagia was 44% at 1 year and 64% at 2 years after trial enrollment for those with spinal onset, and 85% and 92% for those with bulbar onset. The median duration of dysphagia-free survival after trial enrollment was 11.5 months for those with spinal onset and 3.2 months for those with bulbar onset.
Discussion: Our findings underscore the high risk for dysphagia development and support the need for early dysphagia referral and evaluation to minimize the risk of serious dysphagia-related complications.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; dysphagia; incidence; survival; swallowing.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Yang R, Huang R, Chen D, et al. Causes and places of death of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in south-west China. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2011;12(3):206–209. - PubMed
-
- Ruoppolo G, Schettino I, Frasca V, et al. Dysphagia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Prevalence and clinical findings. Acta Neurol Scand. 2013;128(6):397–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous