Social support and siblings of children with cancer: A scoping review
- PMID: 33851490
- PMCID: PMC8363579
- DOI: 10.1002/pon.5689
Social support and siblings of children with cancer: A scoping review
Abstract
Objective: Social support is essential in healthy adjustment to life stressors. This scoping review examines how social support has been conceptualized, operationalized, and studied among siblings of children with cancer. Gaps in the current literature are identified, and future research directions are proposed.
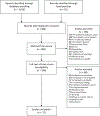
Methods: A rigorous systematic scoping review framework guided our process. Medline, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Scopus were searched for literature regarding social support and siblings of children with cancer. After screening, 57 articles were identified (n = 26 quantitative, n = 21 qualitative, and n = 10 multi-method) and their content extracted for summarization.
Results: The majority of studies (n = 43, 75.4%) were descriptive; 14 (24.6%) included interventions, and of those, four were experimental. Few studies used a clearly defined theoretical framework, or validated tools to measure social support. Studies explored perceived social support needs of siblings, the provision and availability of formal support through interventions and related outcomes, and informal family social supports. A variety of support types were found to be helpful to siblings in different ways.
Conclusions: Social support is a prevalent topic in the literature regarding siblings of children with cancer. It is unclear what types of support are most important due to how it has been conceptualized and measured. Despite some methodological limitations, greater levels of social support have been linked to better adaptation among siblings of children with cancer. Future work is warranted to identify the most beneficial types of support for siblings based on their age, developmental stage, and the cancer trajectory.
Keywords: adaptation; cancer; childhood cancer; neoplasms; oncology; psycho-oncology; psychological; review [scoping]; siblings; social adjustment; social support.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- Woodgate R L. (2006) Siblings’ Experiences with Childhood Cancer: A Different Way of Being in the Family. Cancer Nurs 29 (5):406–414 - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute (2018) Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Cancer (PDQ®). National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/late-effects-pdq.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical