Circuit organization of the excitatory sensorimotor loop through hand/forelimb S1 and M1
- PMID: 33851917
- PMCID: PMC8046433
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66836
Circuit organization of the excitatory sensorimotor loop through hand/forelimb S1 and M1
Abstract
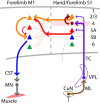
Sensory-guided limb control relies on communication across sensorimotor loops. For active touch with the hand, the longest loop is the transcortical continuation of ascending pathways, particularly the lemnisco-cortical and corticocortical pathways carrying tactile signals via the cuneate nucleus, ventral posterior lateral (VPL) thalamus, and primary somatosensory (S1) and motor (M1) cortices to reach corticospinal neurons and influence descending activity. We characterized excitatory connectivity along this pathway in the mouse. In the lemnisco-cortical leg, disynaptic cuneate→VPL→S1 connections excited mainly layer (L) 4 neurons. In the corticocortical leg, S1→M1 connections from L2/3 and L5A neurons mainly excited downstream L2/3 neurons, which excite corticospinal neurons. The findings provide a detailed new wiring diagram for the hand/forelimb-related transcortical circuit, delineating a basic but complex set of cell-type-specific feedforward excitatory connections that selectively and extensively engage diverse intratelencephalic projection neurons, thereby polysynaptically linking subcortical somatosensory input to cortical motor output to spinal cord.
Keywords: corticospinal; motor; mouse; neocortex; neuroscience; sensorimotor; somatosensory; thalamus.
© 2021, Yamawaki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NY, MR, AS, GS No competing interests declared, GS Gregory A. Smith has disclosed a significant financial interest, Thyreos Inc.The Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Conflict of Interest Review Committees has determined that this must be disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cortico-Thalamo-Cortical Circuits of Mouse Forelimb S1 Are Organized Primarily as Recurrent Loops.J Neurosci. 2020 Apr 1;40(14):2849-2858. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2277-19.2020. Epub 2020 Feb 19. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32075900 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical dynamics in hand/forelimb S1 and M1 evoked by brief photostimulation of the mouse's hand.Elife. 2025 May 19;14:RP105112. doi: 10.7554/eLife.105112. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40387088 Free PMC article.
-
Anterolateral Motor Cortex Connects with a Medial Subdivision of Ventromedial Thalamus through Cell Type-Specific Circuits, Forming an Excitatory Thalamo-Cortico-Thalamic Loop via Layer 1 Apical Tuft Dendrites of Layer 5B Pyramidal Tract Type Neurons.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 10;38(41):8787-8797. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1333-18.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30143573 Free PMC article.
-
Local connections of excitatory neurons in motor-associated cortical areas of the rat.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 May 28;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00075. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23754982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of somatosensory and motor cortex in primates.Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2004 Nov;281(1):1148-56. doi: 10.1002/ar.a.20120. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15470673 Review.
Cited by
-
Axonal Barcode Analysis of Pyramidal Tract Projections from Mouse Forelimb M1 and M2.J Neurosci. 2022 Oct 12;42(41):7733-7743. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1062-22.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 7. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36414009 Free PMC article.
-
An operating principle of the cerebral cortex, and a cellular mechanism for attentional trial-and-error pattern learning and useful classification extraction.Front Neural Circuits. 2024 Mar 5;18:1280604. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2024.1280604. eCollection 2024. Front Neural Circuits. 2024. PMID: 38505865 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between arm and leg neuronal circuits following paired cervical and lumbosacral transspinal stimulation in healthy humans.Exp Brain Res. 2024 Sep;242(9):2229-2239. doi: 10.1007/s00221-024-06891-y. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Exp Brain Res. 2024. PMID: 39034329
-
Multiscale model of primary motor cortex circuits predicts in vivo cell-type-specific, behavioral state-dependent dynamics.Cell Rep. 2023 Jun 27;42(6):112574. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112574. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37300831 Free PMC article.
-
Functional architecture of the forebrain cholinergic system in rodents.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 19:rs.3.rs-4504727. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4504727/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: iScience. 2025 Feb 11;28(3):112001. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112001. PMID: 38947053 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

