Urinary microbiota of women with recurrent urinary tract infection: collection and culture methods
- PMID: 33852041
- PMCID: PMC8514570
- DOI: 10.1007/s00192-021-04780-4
Urinary microbiota of women with recurrent urinary tract infection: collection and culture methods
Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis: Many clinicians utilize standard culture of voided urine to guide treatment for women with recurrent urinary tract infections (RUTI). However, despite antibiotic treatment, symptoms may persist and events frequently recur. The cyclic nature and ineffective treatment of RUTI suggest that underlying uropathogens pass undetected because of the preferential growth of Escherichia coli. Expanded quantitative urine culture (EQUC) detects more clinically relevant microbes. The objective of this study was to assess how urine collection and culture methods influence microbial detection in RUTI patients.
Methods: This cross-sectional study enrolled symptomatic adult women with an established RUTI diagnosis. Participants contributed both midstream voided and catheterized urine specimens for culture via both standard urine culture (SUC) and EQUC. Presence and abundance of microbiota were compared between culture and collection methods.
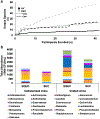
Results: Forty-three symptomatic women participants (mean age 67 years) contributed specimens. Compared to SUC, EQUC detected more unique bacterial species and consistently detected more uropathogens from catheterized and voided urine specimens. For both collection methods, the most commonly detected uropathogens by EQUC were E. coli (catheterized: n = 8, voided: n = 12) and E. faecalis (catheterized: n = 7, voided: n = 17). Compared to catheterized urine samples assessed by EQUC, SUC often missed uropathogens, and culture of voided urines by either method yielded high false-positive rates.
Conclusions: In women with symptomatic RUTI, SUC and assessment of voided urines have clinically relevant limitations in uropathogen detection. These results suggest that, in this population, catheterized specimens analyzed via EQUC provide clinically relevant information for appropriate diagnosis.
Keywords: Enhanced urine culture; Recurrent urinary tract infection; Urinary microbiome; Urinary pathogen detection; Urine collection.
© 2021. The International Urogynecological Association.
Figures
References
-
- Aslam S, Albo M, Brubaker L. Recurrent urinary tract infections in adult women. JAMA. 2020;323(7):658–659. - PubMed
-
- Gaitonde S, Malik RD, Zimmern PE. Financial burden of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: a time-driven activity-based cost analysis. Urol. 2019;128:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Haylen BT, de Ridder D, Freeman RM, Swift SE, Berghmans B, Lee J, Monga A, Petri E, Rizk DE, Sand PK, Schaer GN. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. International Urogynecology J, 2010,21:5–26. - PubMed
-
- Kass EH. Asymptomatic infections of the urinary tract. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1956;69:56–64. - PubMed
-
- Kass EH. Bacteriuria and the diagnosis of infections of the urinary tract; with observations on the use of methionine as a urinary antiseptic. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1957;100(5):709–714. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

