Long noncoding RNA LINC00641 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression via sponging microRNA-340-5p
- PMID: 33853611
- PMCID: PMC8048250
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-01895-y
Long noncoding RNA LINC00641 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression via sponging microRNA-340-5p
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidences have revealed that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have played critical roles in tumor occurrence and progression. LINC00641 has been reported to be involved in the initiation and development of several cancers in the recent years. However, the detailed biological role of LINC00641 in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) remains largely unclear.
Methods: In this study, the expression and biological function of LINC00641 were assessed in renal carcinoma both in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation, migration and colony formation assay were performed to explore the effect of LINC00641on growth, progression and invasion of RCC cell. qRT-PCR, flow cytometry and luciferase reporter assay and in vivo tumorigenicity assay were also carried out.
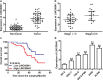
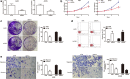
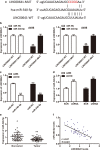
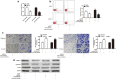
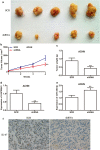
Results: The expression of LINC00641 was overexpressed in RCC tissues and cell lines, and high LINC00641 expression was correlated with tumor-node-metastasis stage. Furthermore, Silencing of LINC00641 remarkably inhibited the ability of cell proliferation, colony formation, and invasive capacities, as well as increasing the apoptotic rates of RCC cells in vitro. Mechanistically, miR-340-5p was validated to be targeted by LINC00641 and knockdown of miR-340-5p counteracted LINC00641 silencing-mediated inhibition of RCC progression. In addition, in vivo experiment confirmed the findings discovered in vitro.
Conclusions: These results suggested that LINC00641 promoted the progression of RCC by sponging miR-340-5p.
Keywords: Cancer progression; LINC00641; Long non-coding RNA; MiR-340-5p; MicroRNA; Renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00641 in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 27;11:829137. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.829137. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35155216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA 00641 Promotes Growth and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer through Regulating miR-450b-5p/GOLPH3 Axis.J Oncol. 2022 Jun 15;2022:8259135. doi: 10.1155/2022/8259135. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35756081 Free PMC article.
-
Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00641 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by sponging miR-194-5p.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Mar;235(3):2668-2675. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29170. Epub 2019 Sep 6. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31490021
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00641 promotes cell growth and migration through modulating miR-378a/ZBTB20 axis in acute myeloid leukemia.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(17):7498-7509. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_18864. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31539138
-
The roles of long non‑coding RNAs in renal cell carcinoma (Review).Mol Clin Oncol. 2022 Nov 28;18(1):4. doi: 10.3892/mco.2022.2600. eCollection 2023 Jan. Mol Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36591597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N6-Methyladenosine-Related Long Non-coding RNA Signature Associated With Prognosis and Immunotherapeutic Efficacy of Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 15;12:726369. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.726369. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34721523 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpressed lncRNA FTX promotes the cell viability, proliferation, migration and invasion of renal cell carcinoma via FTX/miR‑4429/UBE2C axis.Oncol Rep. 2022 Sep;48(3):163. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8378. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35866591 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the role of long non-coding RNA and microRNA network in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its tumor microenvironment.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Feb 2;23(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02861-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 36732762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00641 in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 27;11:829137. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.829137. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35155216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA 00641 Promotes Growth and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer through Regulating miR-450b-5p/GOLPH3 Axis.J Oncol. 2022 Jun 15;2022:8259135. doi: 10.1155/2022/8259135. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35756081 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

