Anthracycline Induced Cardiac Disorders in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Single-Centre, Retrospective, Observational Study
- PMID: 33854429
- PMCID: PMC8039458
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.598708
Anthracycline Induced Cardiac Disorders in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Single-Centre, Retrospective, Observational Study
Abstract
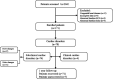
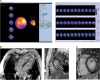
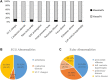
Anthracycline-associated cardiotoxicity is frequently seen in cancer survivors years after treatment, but it is rare in patients on chemotherapy. This study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics of cardiac disorders in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) during chemotherapy. A retrospective case study was conducted in children with ALL, for whom electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiography (Echo) were regularly assessed before each course of chemotherapy. The cardiac disorders were diagnosed according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 5.0. Binary logistic regression analysis was used to identify risk factors associated with cardiac disorders. There were 171 children eligible for the study, and 78 patients (45.61%) were confirmed as having cardiac disorders. The incidence of cardiac disorders was dependent upon the cumulative dose of daunorubicin (DNR) (p = 0.030, OR = 1.553, 95% CI: 1.005-3.108). Four patients (2.34%) presented with palpitation, chest pain, and persistent tachycardia, and they were cured or improved after medical intervention. A total of 74 patients (43.27%) had subclinical cardiac disorders confirmed by ECG or Echo. ECG abnormalities were commonly seen in the induction and continuation treatments, including arrhythmias (26, 15.20%), ST changes (24, 14.04%) and conduction disorders (4, 2.34%). Pericardial effusion (14, 8.19%), left ventricular hypertrophy (11, 6.43%), a widened pulmonary artery (5, 2.92%) and valvular insufficiency (5, 2.92%) suggested by Echo occurred after induction chemotherapy. Therefore, cardiac disorders with clinical manifestations are rare and need early intervention. Subclinical cardiac disorders are common but very hidden in children during ALL chemotherapy. Regular ECG and Echo could help paediatricians to identify and monitor patients with asymptomatic cardiac disorders earlier.
Keywords: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; cardiac disorders; chemotherapy; childhood; daunorubicin.
Copyright © 2021 Yu, Qiu, Yu, Wang, Xu, Peng, Wan, Wu, Jin and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

