Effect of Liraglutide on Cardiometabolic Risk Profile in People with Coronary Artery Disease with or without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 33854433
- PMCID: PMC8039463
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.618208
Effect of Liraglutide on Cardiometabolic Risk Profile in People with Coronary Artery Disease with or without Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
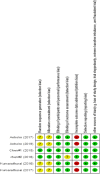
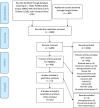
Background: Whether liraglutide use improves cardiometabolic risk factors in different subsets of subjects with coronary artery disease (CAD) remains unclear. In a systematic review and meta-analysis, we quantified the effects of liraglutide on cardiometabolic risk profile in subjects with CAD with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). Methods: Online database searches were conducted in PubMed, Scopus, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane library, and Google Scholar from incept up to 15th January 2021. We identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing the effects of liraglutide compared to placebo on cardiometabolic risk profile. We used the random- or fixed-effect models to pool the weighted mean differences (WMDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results: Out of a total of 7,320 citations, six articles (seven RCTs) with 294 subjects with CAD (mean age, 61.21 years; 19% women) were included. Our findings presented as WMD and 95% CI showed a statistical significant decrease in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) [-0.36%; -0.47; -0.26, p < 0.001; I 2 = 0.0% (with 6 RCTs)], body mass index (BMI) [-0.61 kg/m2; -1.21; -0.01, p = 0.047; I 2 = 72.2% (with five RCTs)], and waist circumference [-2.41 cm; -3.47; -1.36, p < 0.001; I 2 = 0.0% (with three RCTs)]. Through a set of subgroup analyses, we found a significant reduction in BMI in CAD patients with T2D [WMD = -1.06; 95% CI, -1.42, -0.70, p < 0.001; I 2 = 0.0% (with three RCTs)] compared to CAD only patients [WMD = -0.08; 95% CI, -0.45, 0.29, p = 0.66; I 2 = 0.0% (with two RCTs)] in the liraglutide group compared with the placebo group. No significant changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and lipid profiles were observed. Conclusions: Among people with established CAD, liraglutide significantly improved HbA1c, BMI, and waist circumference values. The effect of liraglutide on BMI was more robust in individuals with T2D compared to those without.
Keywords: cardiometabolic profiles; coronary artery disease; liraglutide; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Copyright © 2021 Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, Soroush, Tabrizi, Shabani-Borujeni, Rezaei, Jafari, Hosseini-Bensenjan, Stricker, van Hoek and Ahmadizar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Anholm C., Kumarathurai P., Pedersen L. R., Nielsen O. W., Kristiansen O. P., Fenger M., et al. (2017). Liraglutide effects on beta-cell, insulin sensitivity and glucose effectiveness in patients with stable coronary artery disease and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 19 (6), 850–857. 10.1111/dom.12891 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anholm C., Kumarathurai P., Pedersen L. R., Samkani A., Walzem R. L., Nielsen O. W., et al. (2019). Liraglutide in combination with metformin may improve the atherogenic lipid profile and decrease C-reactive protein level in statin treated obese patients with coronary artery disease and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Atherosclerosis 288, 60–66. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.07.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borenstein M., Hedges L. V., Higgins J. P. T., Rothstein H. R. (2011). Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Buse J. B., Wexler D. J., Tsapas A., Rossing P., Mingrone G., Mathieu C., et al. (2020). 2019 update to: management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Dia Care 43 (2), 487–493. 10.2337/dci19-0066 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen W. R., Hu S. Y., Chen Y. D., Zhang Y., Qian G., Wang J., et al. (2015). Effects of liraglutide on left ventricular function in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am. Heart J. 170 (5), 845–854. 10.1016/j.ahj.2015.07.014 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

