Integrin Activation Enables Sensitive Detection of Functional CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells: Application to Characterize SARS-CoV-2 Immunity
- PMID: 33854501
- PMCID: PMC8040333
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.626308
Integrin Activation Enables Sensitive Detection of Functional CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells: Application to Characterize SARS-CoV-2 Immunity
Abstract
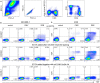
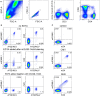
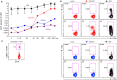
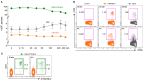
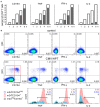
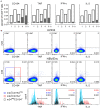
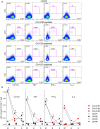
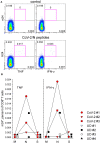
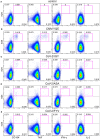
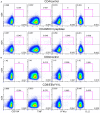
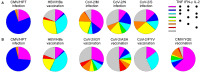
We have previously shown that conformational change in the β2-integrin is a very early activation marker that can be detected with fluorescent multimers of its ligand intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 for rapid assessment of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. In this study, we describe a modified protocol of this assay for sensitive detection of functional antigen-specific CD4+ T cells using a monoclonal antibody (clone m24 Ab) specific for the open, high-affinity conformation of the β2-integrin. The kinetics of β2-integrin activation was different on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (several hours vs. few minutes, respectively); however, m24 Ab readily stained both cell types 4-6 h after antigen stimulation. With this protocol, we were able to monitor ex vivo effector and memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells specific for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and hepatitis B virus (HBV) in whole blood or cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of infected or vaccinated individuals. By costaining β2-integrin with m24 and CD154 Abs, we assessed extremely low frequencies of polyfunctional CD4+ T cell responses. The novel assay used in this study allows very sensitive and simultaneous screening of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cell reactivities, with versatile applicability in clinical and vaccination studies.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells; CD8+ T cells; SARS-CoV-2; antigen specificity; integrin activation.
Copyright © 2021 Schöllhorn, Schuhmacher, Besedovsky, Fendel, Jensen, Stevanović, Lange, Rammensee, Born, Gouttefangeas and Dimitrov.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Longitudinal Analysis of Human Memory T-Cell Response According to the Severity of Illness up to 8 Months After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection.J Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 2;224(1):39-48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab159. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33755725 Free PMC article.
-
Suboptimal SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T cell response associated with the prominent HLA-A*02:01 phenotype.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 29;117(39):24384-24391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2015486117. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32913053 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of IFNγ-Secreting CD4+ and CD8+ Memory T Cells in COVID-19 Convalescents after Stimulation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells with Live SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2021 Jul 29;13(8):1490. doi: 10.3390/v13081490. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452355 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Related Dynamics of Lung-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells in the Age of COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 29;12:636118. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636118. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33854506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypes and Functions of SARS-CoV-2-Reactive T Cells.Mol Cells. 2021 Jun 30;44(6):401-407. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0079. Mol Cells. 2021. PMID: 34120892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MOSPD2 regulates the activation state of αLβ2 integrin to control monocyte migration: applicability for treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases.Immunol Res. 2025 May 1;73(1):78. doi: 10.1007/s12026-025-09633-6. Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 40312574 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of β2 integrin activation by talin unveils subunit-specific mechanisms of integrin signaling.Cell Rep. 2025 May 27;44(5):115607. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115607. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40310722 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 10;13:1001198. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1001198. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36300105 Free PMC article.
-
Development of humoral and cellular immunological memory against SARS-CoV-2 despite B cell depleting treatment in multiple sclerosis.iScience. 2021 Sep 24;24(9):103078. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103078. Epub 2021 Sep 2. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34490414 Free PMC article.
-
PCI-DB: a novel primary tissue immunopeptidome database to guide next-generation peptide-based immunotherapy development.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Apr 15;13(4):e011366. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-011366. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40234091 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

