Polyphony of domestic dog whines and vocal cues to body size
- PMID: 33854534
- PMCID: PMC8026154
- DOI: 10.1093/cz/zoaa042
Polyphony of domestic dog whines and vocal cues to body size
Abstract
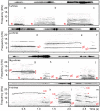
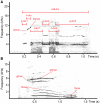
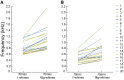
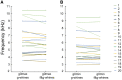
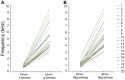
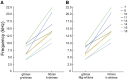
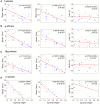
In domestic dogs Canis familiaris, vocal traits have been investigated for barks and growls, and the relationship between individual body size and vocal traits investigated for growls, with less corresponding information for whines. In this study, we examined the frequency and temporal traits of whines of 20 adult companion dogs (9 males, 11 females), ranging in body mass from 3.5 to 70.0 kg and belonging to 16 breeds. Dog whines (26-71 per individual, 824 in total) were recorded in conditioned begging contexts modeled by dog owners. Whines had 3 independent fundamental frequencies: the low, the high and the ultra-high that occurred singly as monophonic calls or simultaneously as 2-voice biphonic or 3-voice polyphonic calls. From the smallest to largest dog, the upper frequency limit varied from 0.24 to 2.13 kHz for the low fundamental frequency, from 2.95 to 10.46 kHz for the high fundamental frequency and from 9.99 to 23.26 kHz for the ultra-high fundamental frequency. Within individuals, the low fundamental frequency was lower in monophonic than in biphonic whines, whereas the high fundamental frequency did not differ between those whine types. All frequency variables of the low, high, and ultra-high fundamental frequencies correlated negatively with dog body mass. For duration, no correlation with body mass was found. We discuss potential production mechanisms and sound sources for each fundamental frequency; point to the acoustic similarity between high-frequency dog whines and rodent ultrasonic calls and hypothesize that ultra-high fundamental frequencies function to allow private, "tete-a-tete" communication between members of social groups.
Keywords: Canis familiaris; acoustic communication; companion dogs; high-frequency calls; nonlinear phenomena; vocalization.
© The Author(s) (2020). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Editorial Office, Current Zoology.
Figures
References
-
- Alipour F, Scherer RC, Finnegan EM, 1997. Pressure-flow relationship during phonation as a function of adduction. J Voice 11:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Alipour F, Jaiswal S, Finnegan EM, 2007. Aerodynamic and acoustic effects of false folds and epiglottis in excised larynx models. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 116:135–144. - PubMed
-
- Amiot C, Bastian B, Martens P, 2016. People and companion animals: it takes two to tango. BioScience 66:552–560.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
