Efficacy and Safety of Ningmitai Capsules in Patients with Chronic Epididymitis: A Prospective, Parallel Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33854561
- PMCID: PMC8021469
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9752592
Efficacy and Safety of Ningmitai Capsules in Patients with Chronic Epididymitis: A Prospective, Parallel Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Ningmitai (NMT) capsules in patients with chronic epididymitis.
Methods: This prospective randomized controlled trial included 112 patients diagnosed with chronic epididymitis. The patients were randomized (1 : 1 : 1) to receive levofloxacin (LVX), NMT, or NMT combined with LVX for 4 weeks. The patients were followed up at 2 and 4 weeks after initiation of treatment and were evaluated in terms of Chronic Epididymitis Symptom Index (CESI) scores, epididymal nodules, and safety parameters. The primary endpoints were the CESI scores at the end of 2 and 4 weeks of treatment. The secondary endpoints included the mean epididymal nodule diameter and the clinical efficacy rate. Safety was evaluated by hepatorenal function tests and adverse event reports during the trial.
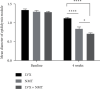
Results: After 2 weeks of treatment, the CESI score of the NMT group was significantly lower than that of the LVX group (P < 0.05). In addition, the clinical efficacy rate of the NMT group was significantly higher than that of the LVX group (55% vs. 8.33%, P < 0.0001), indicating that NMT has a rapid effect on chronic epididymitis. After 4 weeks of treatment, there was no significant difference in CESI scores or clinical efficacy rates between the two monotherapy regimens (P > 0.05); however, the mean diameter of epididymal nodules was significantly smaller in the NMT group than in the LVX group (P < 0.0001). Moreover, after 4 weeks of treatment, the patients in the LVX + NMT group, which had a clinical efficacy rate of 97.22%, had lower CESI scores (both P < 0.01) and a smaller epididymal nodule diameter (vs. LVX, P < 0.0001; vs. NMT, P < 0.05) than those in the other two groups. No adverse events or abnormal hepatorenal function were found during the study.
Conclusion: NMT significantly improved CESI scores and epididymal nodule diameter in patients with chronic epididymitis. The combination of NMT and LVX provides a much better effect than monotherapy, and this treatment regimen was well tolerated.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang Jing et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim M. K., Leem J., Kim Y. I., et al. Gyejigachulbutang (Gui-Zhi-Jia-Shu-Fu-Tang, Keishikajutsubuto, TJ-18) in degenerative knee osteoarthritis patients: lessons and responders from a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2020;2020:11. doi: 10.1155/2020/2376581.2376581 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shakeri A., Hashempur M. H., Mojibian M., Aliasl F., Bioos S., Nejatbakhsh F. A comparative study of ranitidine and quince (Cydonia oblonga mill) sauce on gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in pregnancy: a randomised, open-label, active-controlled clinical trial. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 2018;38(7):899–905. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2018.1431210. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources