Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins play the roles of radioprotection on Normal Lung and radiosensitization on Lung Cancer via differential regulation of the MAPK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33854585
- PMCID: PMC8040900
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.49987
Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins play the roles of radioprotection on Normal Lung and radiosensitization on Lung Cancer via differential regulation of the MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
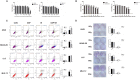
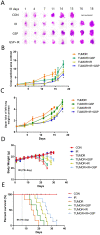
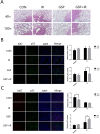
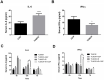
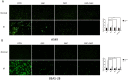
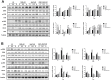
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a common serious complication and dose-limiting factor caused by radiotherapy for lung cancer. This study was to investigate radioprotective effects of grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSP) on normal lung as well as radiosensitizing effects on lung cancer. In vitro, we demonstrated radioprotective effects of GSP on normal alveolar epithelial cells (MLE-12 and BEAS/2B) and radiosensitizing effects on lung cancer cells (LLC and A549). In vivo, we confirmed these two-way effects in tumor-bearing mice. The results showed that GSP inhibited tumor growth, and played a synergistic killing effect with radiotherapy on lung cancer. Meanwhile, GSP reduced radiation damage to normal lung tissues. The two-way effects related to the differential regulation of the MAPK signaling pathway by GSP on normal lung and lung cancer. Moreover, GSP regulated secretion of cytokines IL-6 and IFN-γ and expression of p53 and Ki67 on normal lung and lung cancer. Our findings suggest that GSP is expected to be an ideal radioprotective drug for lung cancer patients who are treated with radiotherapy.
Keywords: MAPK; Proanthocyanidins; lung cancer; radioprotection; radiosensitization.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB. et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(5):363–385. - PubMed
-
- Stahl JM, Corso CD, Verma V. et al. Trends in stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2017;103:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Kong FM, Hayman JA, Griffith KA. et al. Final toxicity results of a radiation-dose escalation study in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): predictors for radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65(4):1075–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

