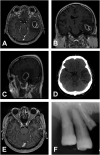
Fusobacterium nucleatum-caused brain abscess - Case report
- PMID: 33854732
- PMCID: PMC8025227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.01.007
Fusobacterium nucleatum-caused brain abscess - Case report
Keywords: Brain abscess; Fusobacterium nucleatum; Oral cavity; Periodontal pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Kenig A., Kessler A., Alaa S. An immunocompetent patient with culture-negative multiple brain abscesses caused by Fusobacterium nucleatum. Case Rep. 2020;65:102261. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

