Tailor-Made Nanomaterials for Diagnosis and Therapy of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33854877
- PMCID: PMC8025024
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202002545
Tailor-Made Nanomaterials for Diagnosis and Therapy of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
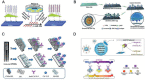
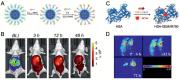
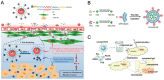
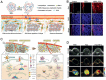
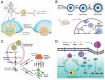
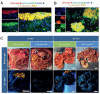
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide due to its aggressiveness and the challenge to early diagnosis and treatment. In recent decades, nanomaterials have received increasing attention for diagnosis and therapy of PDAC. However, these designs are mainly focused on the macroscopic tumor therapeutic effect, while the crucial nano-bio interactions in the heterogeneous microenvironment of PDAC remain poorly understood. As a result, the majority of potent nanomedicines show limited performance in ameliorating PDAC in clinical translation. Therefore, exploiting the unique nature of the PDAC by detecting potential biomarkers together with a deep understanding of nano-bio interactions that occur in the tumor microenvironment is pivotal to the design of PDAC-tailored effective nanomedicine. This review will introduce tailor-made nanomaterials-enabled laboratory tests and advanced noninvasive imaging technologies for early and accurate diagnosis of PDAC. Moreover, the fabrication of a myriad of tailor-made nanomaterials for various PDAC therapeutic modalities will be reviewed. Furthermore, much preferred theranostic multifunctional nanomaterials for imaging-guided therapies of PDAC will be elaborated. Lastly, the prospects of these nanomaterials in terms of clinical translation and potential breakthroughs will be briefly discussed.
Keywords: diagnosis; imaging‐guided therapy; nanomaterials; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; therapy.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Riquelme E., Zhang Y., Zhang L., Montiel M., Zoltan M., Dong W., Quesada P., Sahin I., Chandra V., San Lucas A., Scheet P., Xu H., Hanash S. M., Feng L., Burks J. K., Do K.‐A., Peterson C. B., Nejman D., Tzeng C.‐W. D., Kim M. P., Sears C. L., Ajami N., Petrosino J., Wood L. D., Maitra A., Straussman R., Katz M., White J. R., Jenq R., Wargo J., McAllister F., Cell 2019, 178, 795. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T., Wood L. D., Itoi T., Takaori K., Lancet 2016, 388, 73. - PubMed
-
- Kim D. W., Kim S. Y., Kim H. K., Kim S. W., Shin S. W., Kim J. S., Park K., Lee M. Y., Heo D. S., Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
