TRPC1 Inhibits Cell Proliferation/Invasion and Is Predictive of a Better Prognosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 33854967
- PMCID: PMC8039442
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.627713
TRPC1 Inhibits Cell Proliferation/Invasion and Is Predictive of a Better Prognosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: TRPC1 Inhibits Cell Proliferation/Invasion and Is Predictive of a Better Prognosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 6;11:767805. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.767805. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34692552 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background and objectives: In China, over 90% of esophageal cancer (EC) cases are esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). ESCC is a frequently malignant tumor with poor prognosis despite the development of comprehensive therapeutic strategies, for which there is still a lack of effective prognostic factors. Previous studies found that the abnormal expression of TRPC1 is closely related to the proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and differentiation of various tumors. However, the relationship between TRPC1 and ESCC is currently unclear. The present study aimed to clarify the clinical significance of TRPC1 and to preliminarily assess the molecular mechanism by which TRPC1 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in ESCC.
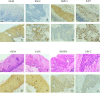
Materials and methods: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to determine the expression of TRPC1 and Ki-67 in 165 cases of ESCC. The correlations between TRPC1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics were determined, and both univariate and multivariate analyses were utilized to quantify the impact of TRPC1 expression on patient survival. Cell Counting Kit-8, scratch wound healing, and transwell assays were used to determine the effects of TRPC1 on proliferation, migration, and invasion in ESCC in vitro, respectively.
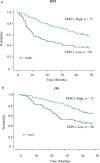
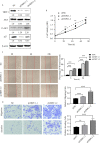
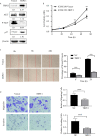
Results: The positive expression rate of TRPC1 showed significantly decreased in ESCC (45.50%) compared with the levels in normal esophageal mucosa (NEM; 80.80%) and high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (HGIEN; 63.20%) (P<0.001). Higher expression rate of TRPC1 was associated with low lymph node metastasis (P<0.001), high differentiation (rs = 0.232, P=0.003), and low Ki-67 (rs = -0.492, P<0.001). We further revealed that low expression of TRPC1 was associated with poor prognosis (Disease-free survival, DFS: 95% CI=0.545-0.845, P=0.001; Overall survival, OS: 95% CI=0.553-0.891, P=0.004). Furthermore, we showed that downregulation of TRPC1 promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line EC9706 in vitro. In contrast, overexpression of TRPC1 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line KYSE150 (P<0.01), in a manner at least in part mediated through the AKT/p27 pathway.
Conclusion: TRPC1 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of EC9706 and KYSE150 cells, at least, in part mediated through the AKT/p27 pathway in vitro. The downregulation of TRPC1 may be one of the most important molecular events in the malignant progression of ESCC. TRPC1 could be a new candidate tumor suppressor gene and a new prognostic factor of ESCC.
Keywords: TRPC1; cell proliferation; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; migration and invasion; prognosis.
Copyright © 2021 Zeng, Zhang, Chen, Zhang, Gao, Lin, Huang, Zhang and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Luo ML, Shen XM, Zhang Y, Wei F, Xu X, Cai Y, et al. Amplification and overexpression of CTTN (EMS1) contribute to the metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by promoting cell migration and anoikis resistance. Cancer Res (2006) 66(24):11690. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1484 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

