Glycemic control, associated factors, acute complications of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in children, adolescents and young adults in Tanzania
- PMID: 33855206
- PMCID: PMC8029575
- DOI: 10.1002/edm2.200
Glycemic control, associated factors, acute complications of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in children, adolescents and young adults in Tanzania
Abstract
Objective: To determine the factors associated with poor glycemic control in children (1-10 years), adolescents (11-18 years) and young adults (19-40 years) with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) in Kilimanjaro Christian Medical Center (KCMC) in Moshi, Mount Meru Regional Referral Hospital (MMRRH) and Meru District Hospital (MDH) in Arusha, Tanzania.
Methods: Cross sectional study of 150 participants conducted from January to June 2019, data was collected by structured questionnaire and analyzed using SPSS version 23.
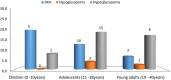
Results: The mean HbA1c was 12.3 ± 2.2%, 146 had poor glycemic control (HbA1c > 7.5%). BMI, insulin regime and caretaker education were associated with poor glycemic control. There were 16 participants diagnosed in DKA and the most frequently reported complications in the prior 3 months were hyperglycemia (n = 25), DKA (n = 18) and hypoglycemia (n = 4).
Conclusions: Glycemic control is still very poor particularly in adolescents. Significant associations with glycemic control were higher BMI, insulin regime and guardian education. The study revealed lower prevalence of DKA at diagnosis compared to previous studies.
Keywords: acute complications; associated factors; glycemic control.
© 2020 The Authors. Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no financial relationships or conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Dimeglio LA, Acerini CL, Codner E, et al. 2018 ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines Glycemic control targets and glucose monitoring for children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018;9:105‐114. - PubMed
-
- World health Organisation . Global Report on Diabetes. 2016;978, 88. ISBN 978 92 4 156525 7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

