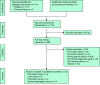
Breath analysis for the detection of digestive tract malignancies: systematic review
- PMID: 33855362
- PMCID: PMC8047095
- DOI: 10.1093/bjsopen/zrab013
Breath analysis for the detection of digestive tract malignancies: systematic review
Abstract
Background: In recent decades there has been growing interest in the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath as biomarkers for the diagnosis of multiple variants of cancer. This review aimed to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy and current status of VOC analysis in exhaled breath for the detection of cancer in the digestive tract.
Methods: PubMed and the Cochrane Library database were searched for VOC analysis studies, in which exhaled air was used to detect gastro-oesophageal, liver, pancreatic, and intestinal cancer in humans, Quality assessment was performed using the QUADAS-2 criteria. Data on diagnostic performance, VOCs with discriminative power, and methodological information were extracted from the included articles.
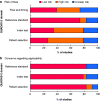
Results: Twenty-three articles were included (gastro-oesophageal cancer n = 14, liver cancer n = 1, pancreatic cancer n = 2, colorectal cancer n = 6). Methodological issues included different modalities of patient preparation and sampling and platform used. The sensitivity and specificity of VOC analysis ranged from 66.7 to 100 per cent and from 48.1 to 97.9 per cent respectively. Owing to heterogeneity of the studies, no pooling of the results could be performed. Of the VOCs found, 32 were identified in more than one study. Nineteen were reported as cancer type-specific, whereas 13 were found in different cancer types. Overall, decanal, nonanal, and acetone were the most frequently identified.
Conclusion: The literature on VOC analysis has documented a lack of standardization in study designs. Heterogeneity between the studies and insufficient validation of the results make interpretation of the outcomes challenging. To reach clinical applicability, future studies on breath analysis should provide an accurate description of the methodology and validate their findings.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of BJS Society Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424 - PubMed
-
- Hawkes N. Cancer survival data emphasise importance of early diagnosis. BMJ 2019;364:l408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources