SARS-CoV-2 one year on: evidence for ongoing viral adaptation
- PMID: 33855951
- PMCID: PMC8290271
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001584
SARS-CoV-2 one year on: evidence for ongoing viral adaptation
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 is thought to have originated in the human population from a zoonotic spillover event. Infection in humans results in a variety of outcomes ranging from asymptomatic cases to the disease COVID-19, which can have significant morbidity and mortality, with over two million confirmed deaths worldwide as of January 2021. Over a year into the pandemic, sequencing analysis has shown that variants of SARS-CoV-2 are being selected as the virus continues to circulate widely within the human population. The predominant drivers of genetic variation within SARS-CoV-2 are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) caused by polymerase error, potential host factor driven RNA modification, and insertion/deletions (indels) resulting from the discontinuous nature of viral RNA synthesis. While many mutations represent neutral 'genetic drift' or have quickly died out, a subset may be affecting viral traits such as transmissibility, pathogenicity, host range, and antigenicity of the virus. In this review, we summarise the current extent of genetic change in SARS-CoV-2, particularly recently emerging variants of concern, and consider the phenotypic consequences of this viral evolution that may impact the future trajectory of the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; adaptation; coronavirus; mutant; pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

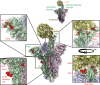
References
-
- News B Coronavirus confirmed as pandemic by World Health Organization bbc.co.uk: BBC. 2020 https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-51839944
-
- World Health Organisation WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/2021
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

