Estimating the Proportion of COVID-19 Contacts Among Households Based on Individuals With Myocardial Infarction History: Cross-sectional Telephone Survey
- PMID: 33855968
- PMCID: PMC8083951
- DOI: 10.2196/26955
Estimating the Proportion of COVID-19 Contacts Among Households Based on Individuals With Myocardial Infarction History: Cross-sectional Telephone Survey
Abstract
Background: Adults with cardiovascular diseases were disproportionately associated with an increased risk of a severe form of COVID-19 and all-cause mortality.
Objective: The aims of this study are to report the associated symptoms for COVID-19 cases, to estimate the proportion of contacts, and to describe the clinical signs and behaviors among individuals with and without myocardial infarction history among cases and contacts.
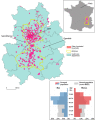
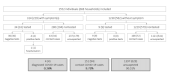
Methods: A 2-week cross-sectional telephone survey was conducted during the first lockdown period in France, from May 4 to 15, 2020. A total of 668 households participated, representing 703 individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular disease in the past 2 years and 849 individuals without myocardial infarction history.
Results: High rates of compliance with health measures were self-reported, regardless of age or risk factors. There were 4 confirmed COVID-19 cases that were registered from 4 different households. Based on deductive assumptions of the 1552 individuals, 9.73% (n=151) were identified as contacts, of whom 71.52% (108/151) were asymptomatic. Among individuals with a myocardial infarction history, 2 were COVID-19 cases, and the estimated proportion of contacts was 8.68% (61/703), of whom 68.85% (42/61) were asymptomatic. The cases and contacts presented different symptoms, with more respiratory signs in those with a myocardial infarction history.
Conclusions: The telephone survey could be a relevant tool for reporting the number of contacts during a limited period and in a limited territory based on the presence of associated symptoms and COVID-19 cases in the households. This study advanced our knowledge to better prepare for future crises.
Keywords: COVID-19; cardiovascular; cases; contacts; cross-sectional; estimate; household; myocardial infarction; risk; survey; symptom.
©Laurie Fraticelli, Julie Freyssenge, Clément Claustre, Mikaël Martinez, Abdesslam Redjaline, Patrice Serre, Thomas Bochaton, Carlos El Khoury. Originally published in JMIR Formative Research (https://formative.jmir.org), 27.04.2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Household secondary attack rate of COVID-19 and associated determinants in Guangzhou, China: a retrospective cohort study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;20(10):1141-1150. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30471-0. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32562601 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of COVID-19 in Bangladesh, April to October 2020-a cross-sectional study.IJID Reg. 2021 Dec;1:92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2021.10.003. Epub 2021 Oct 14. IJID Reg. 2021. PMID: 35721768 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-sectional survey of compliance behaviour, knowledge and attitudes among cases and close contacts during COVID-19 pandemic.Public Health Pract (Oxf). 2023 Jun;5:100370. doi: 10.1016/j.puhip.2023.100370. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Public Health Pract (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 36817733 Free PMC article.
-
Asymptomatic Infection and Transmission of Pertussis in Households: A Systematic Review.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Jan 1;70(1):152-161. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz531. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31257450
-
Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction in Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Sep 28;21:e926101. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.926101. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32981926 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. World Health Organization. 2021. [2021-02-05]. https://covid19.who.int/
-
- COVID-19 Point épidémiologique - Situation au 10 mars 2020 à minuit. Santé publique France. 2021. [2021-02-05]. https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/content/download/236267/2530148#:~:te....
-
- Point épidémio régional Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Spécial COVID-19 7 mai 2020. Santé publique France. 2021. [2020-02-05]. https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/content/download/250727/2594944.
-
- Ceylan Z. Estimation of COVID-19 prevalence in Italy, Spain, and France. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Aug 10;729:138817. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138817. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32360907 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fang Y, Zhang H, Xie J, Lin M, Ying L, Pang P, Ji W. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology. 2020 Aug;296(2):E115–E117. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200432. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32073353 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

