Spike Antibody Levels of Nursing Home Residents With or Without Prior COVID-19 3 Weeks After a Single BNT162b2 Vaccine Dose
- PMID: 33856406
- PMCID: PMC8050783
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2021.6042
Spike Antibody Levels of Nursing Home Residents With or Without Prior COVID-19 3 Weeks After a Single BNT162b2 Vaccine Dose
Abstract
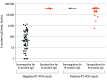
This study compares IgG antibody levels after a single dose of the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccine in nursing home residents with vs without prior COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

