Effect of an electronic nicotine delivery system with 0, 8, or 36 mg/mL liquid nicotine versus a cigarette substitute on tobacco-related toxicant exposure: a four-arm, parallel-group, randomised, controlled trial
- PMID: 33857436
- PMCID: PMC8349799
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00022-9
Effect of an electronic nicotine delivery system with 0, 8, or 36 mg/mL liquid nicotine versus a cigarette substitute on tobacco-related toxicant exposure: a four-arm, parallel-group, randomised, controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDSs) are used by some smokers to reduce cigarette consumption, but their effectiveness is uncertain. We aimed to examine the extent to which ENDSs or a non-nicotine cigarette substitute influence tobacco-related toxicant exposure and cigarette consumption in smokers interested in smoking reduction.
Methods: We did a four-arm, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial at two sites in the USA (Penn State University, Hershey, PA, and Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA). We enrolled adults aged 21-65 years who smoked more than nine cigarettes per day (for at least the past year), with exhaled CO of more than 9 parts per million at screening, who were not currently using an ENDS, and who were interested in reducing smoking but not quitting. Participants were randomised (site-specific with allocation concealment; 1:1:1:1) to receive either a cartomiser-based, pen-style ENDS (eGo-style) paired with 0, 8, or 36 mg/mL liquid nicotine (participants and researchers masked to concentration) or a non-ENDS cigarette-shaped plastic tube that delivered no nicotine or aerosol (cigarette substitute; unmasked) for 24 weeks. Conditions were chosen to reflect a range of nicotine delivery including none (cigarette substitute and 0 mg/mL ENDS), low (8 mg/mL), and cigarette-like (36 mg/mL), and all conditions were paired with smoking reduction instructions. The primary outcome was concentration of the tobacco-specific carcinogen metabolite 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL; urinary total) collected at randomisation and at 4, 12, and 24 weeks. Multiple imputation with and without covariate adjustment was used in addition to sensitivity analyses. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02342795.
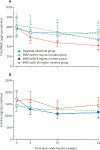
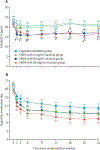
Findings: Between July 22, 2015, and Nov 16, 2017, 684 individuals were screened and 520 (76%) were enrolled and randomised. 188 (36%) of 520 participants were lost to follow-up by week 24; attrition did not differ by study group (39 [30%] of 130 in the cigarette substitute group, 56 [43%] of 130 in the ENDS with 0 mg/mL nicotine group, 49 [38%] of 130 in the ENDS 8 mg/mL group, and 44 [34%] of 130 in the ENDS 36 mg/mL group). Urinary total NNAL at 24 weeks in the ENDS with 36 mg/mL nicotine group was 210·80 pg/mg creatinine (95% CI 163·03-274·42) compared with 346·09 pg/mg creatinine (265·00-455·32) in the cigarette substitute group (p=0·0061). No other significant differences between groups were observed for any time point for urinary total NNAL. Serious adverse event frequency was similar across groups (12 events in 12 participants [9%] in the ENDS with 36 mg/mL nicotine group, seven events in six participants [5%] in the 8 mg/mL group, 11 events in ten participants [8%] in the 0 mg/mL group, and 13 events in 13 participants [10%] in the cigarette substitute group), and all of these were deemed unrelated or unlikely to be related to study product use. There was one death between randomisation and 24 weeks (suicide; in the ENDS with 0 mg/mL nicotine group).
Interpretation: Use of an ENDS with cigarette-like nicotine delivery can reduce exposure to a major pulmonary carcinogen, NNAL, even with concurrent smoking. Future ENDS trials should involve products with well characterised nicotine delivery, including those with nicotine delivery approaching that of a cigarette.
Funding: National Institutes of Health, US Food and Drug Administration.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests COC reports grants from National Institute on Drug Abuse and US Food and Drug Administration, during the conduct of the study. JF reports grants from National Institute on Drug Abuse and US Food and Drug Administration, during the conduct of the study, and grants, personal fees, and non-financial support from Pfizer, outside of the submitted work. AAL reports grants from National Institute on Drug Abuse and US Food and Drug Administration, during the conduct of the study. JMY reports grants from National Institute on Drug Abuse and US Food and Drug Administration, during the conduct of the study. LK reports grants from National Institute on Drug Abuse and US Food and Drug Administration, during the conduct of the study. SV reports grants from National Institute on Drug Abuse and US Food and Drug Administration, during the conduct of the study. CB has previously undertaken trials of electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation (with electronic cigarettes purchased from an online retailer [NZVAPOR], electronic cigarette liquid for one trial purchased from Nicopharm, Australia, and nicotine patches supplied by the New Zealand Government via their contract with Novartis [Sydney, Australia]). Neither NZVAPOR nor Nicopharm have links with the tobacco industry. None of these parties had any role in the design, conduct, analysis, or interpretation of the trial findings, or writing of this publication. TE reports grants from National Institute on Drug Abuse and US Food and Drug Administration, during the conduct of the study, and is a paid consultant in litigation against the tobacco industry and also the electronic cigarette industry and is named on one patent for a device that measures the puffing behavior of electronic cigarette users and on another patent for a smartphone application that determines electronic cigarette device and liquid characteristics. M-SY reports grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the US Food and Drug Administration, during the conduct of the study.
Figures

Comment in
-
E-cigarettes for smoking reduction: a piece of the public health puzzle.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Aug;9(8):804-805. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00071-0. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 33857434 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice; Committee on the Review of the Health Effects of Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems. Public health consequences of e-cigarettes. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2018.
-
- Bullen C, Howe C, Laugesen M, et al. Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2013; 382: 1629–37. - PubMed
-
- Walker N, Parag V, Verbiest M, Laking G, Laugesen M, Bullen C. Nicotine patches used in combination with e-cigarettes (with and without nicotine) for smoking cessation: a pragmatic, randomised trial. Lancet Respir Med 2020; 8: 54–64. - PubMed
-
- Hajek P, Phillips-Waller A, Przulj D, et al. A randomized trial of e-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement therapy. N Engl J Med 2019; 380: 629–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

