Sarcoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria communication; implications for cardiac arrhythmia
- PMID: 33857485
- PMCID: PMC8217367
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.04.002
Sarcoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria communication; implications for cardiac arrhythmia
Abstract
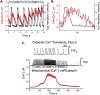
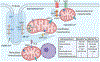
Sudden cardiac death due to ventricular tachyarrhythmias remains the major cause of mortality in the world. Heart failure, diabetic cardiomyopathy, old age-related cardiac dysfunction and inherited disorders are associated with enhanced propensity to malignant cardiac arrhythmias. Both defective mitochondrial function and abnormal intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis have been established as the key contributing factors in the pathophysiology and arrhythmogenesis in these conditions. This article reviews current advances in understanding of bidirectional control of ryanodine receptor-mediated sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release and mitochondrial function, and how defects in crosstalk between these two organelles increase arrhythmic risk in cardiac disease.
Keywords: Calcium signaling; Cardiac arrhythmia; Mitochondria; Sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bers DM. Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Cardiac Contractile Force. Springer; Netherlands. 2001.
-
- Bers DM. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 2002; 415(6868): 198–205. - PubMed
-
- Fill M, Copello JA. Ryanodine receptor calcium release channels. Physiol Rev. 2002; 82(4): 893–922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

