Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Outcomes in CKD: Findings From the CRIC Study
- PMID: 33857532
- PMCID: PMC8316276
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.01.020
Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Outcomes in CKD: Findings From the CRIC Study
Abstract
Rationale & objective: Cardiovascular events are less common in women than men in general populations; however, studies in chronic kidney disease (CKD) are less conclusive. We evaluated sex-related differences in cardiovascular events and death in adults with CKD.
Study design: Prospective cohort study.
Setting & participants: 1,778 women and 2,161 men enrolled in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC).
Exposure: Sex (women vs men).
Outcome: Atherosclerotic composite outcome (myocardial infarction, stroke, or peripheral artery disease), incident heart failure, cardiovascular death, and all-cause death.
Analytical approach: Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results: During a median follow-up period of 9.6 years, we observed 698 atherosclerotic events (women, 264; men, 434), 762 heart failure events (women, 331; men, 431), 435 cardiovascular deaths (women, 163; men, 274), and 1,158 deaths from any cause (women, 449; men, 709). In analyses adjusted for sociodemographic, clinical, and metabolic parameters, women had a lower risk of atherosclerotic events (HR, 0.71 [95% CI, 0.57-0.88]), heart failure (HR, 0.76 [95% CI, 0.62-0.93]), cardiovascular death (HR, 0.55 [95% CI, 0.42-0.72]), and death from any cause (HR, 0.58 [95% CI, 0.49-0.69]) compared with men. These associations remained statistically significant after adjusting for cardiac and inflammation biomarkers.
Limitations: Assessment of sex hormones, which may play a role in cardiovascular risk, was not included.
Conclusions: In a large, diverse cohort of adults with CKD, compared with men, women had lower risks of cardiovascular events, cardiovascular mortality, and mortality from any cause. These differences were not explained by measured cardiovascular risk factors.
Keywords: Atherosclerotic event; cardiac biomarker; cardiovascular disease (CVD); cardiovascular outcomes; chronic kidney disease (CKD); female; heart failure; male; mortality; myocardial infarction (MI); risk assessment; sex differences; sex factors.
Copyright © 2021 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
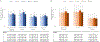

Comment in
-
Do Sex and Gender Matter in Kidney and Cardiovascular Disease?Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Aug;78(2):177-179. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.05.002. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 34120781 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jousilahti P, Vartiainen E, Tuomilehto J, Puska P. Sex, age, cardiovascular risk factors, and coronary heart disease: a prospective follow-up study of 14 786 middle-aged men and women in Finland. Circulation. 1999;99(9):1165–1172. - PubMed
-
- Lerner DJ, Kannel WB. Patterns of coronary heart disease morbidity and mortality in the sexes: a 26-year follow-up of the Framingham population. Am Heart J. 1986;111(2):383–390. - PubMed
-
- Wingard DL, Suarez L, Barrett-Connor E. The sex differential in mortality from all causes and ischemic heart disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1983;117(2):165–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR002548/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104940/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119199/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK094829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK092290/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127028/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK072231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK118736/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM109036/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

