Nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs) as molecular tools to direct desirable and avoid undesirable immunological effects
- PMID: 33857556
- PMCID: PMC8178219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.04.011
Nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs) as molecular tools to direct desirable and avoid undesirable immunological effects
Abstract
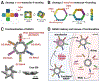
Nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs) represent a highly versatile molecular platform for the targeted delivery of various therapeutics. However, despite their promise, further clinical translation of this innovative technology can be hindered by immunological off-target effects. All human cells are equipped with an arsenal of receptors that recognize molecular patterns specific to foreign nucleic acids and understanding the rules that guide this recognition offer the key rationale for the development of therapeutic NANPs with tunable immune stimulation. Numerous recent studies have provided increasing evidence that in addition to NANPs' physicochemical properties and therapeutic effects, their interactions with cells of the immune system can be regulated through multiple independently programmable architectural parameters. The results further suggest that defined immunomodulation by NANPs can either support their immunoquiescent delivery or be used for conditional stimulation of beneficial immunological responses.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Immune responses; Immunostimulation; Immunotherapy; NANPs; PRR; RNA nanotechnology.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Wang F, Zuroske T, Watts JK, RNA therapeutics on the rise, Nat Rev Drug Discov, 19 (2020) 441–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

