Interleukin 8 Elicits Rapid Physiological Changes in Neutrophils That Are Altered by Inflammatory Conditions
- PMID: 33857948
- PMCID: PMC8460987
- DOI: 10.1159/000514885
Interleukin 8 Elicits Rapid Physiological Changes in Neutrophils That Are Altered by Inflammatory Conditions
Abstract
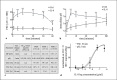
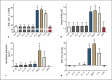
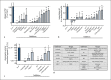
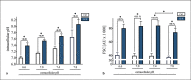
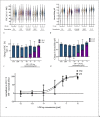
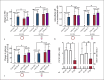
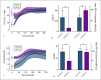
A sufficient response of neutrophil granulocytes stimulated by interleukin (IL)-8 is vital during systemic inflammation, for example, in sepsis or severe trauma. Moreover, IL-8 is clinically used as biomarker of inflammatory processes. However, the effects of IL-8 on cellular key regulators of neutrophil properties such as the intracellular pH (pHi) in dependence of ion transport proteins and during inflammation remain to be elucidated. Therefore, we investigated in detail the fundamental changes in pHi, cellular shape, and chemotactic activity elicited by IL-8. Using flow cytometric methods, we determined that the IL-8-induced cellular activity was largely dependent on specific ion channels and transporters, such as the sodium-proton exchanger 1 (NHE1) and non-NHE1-dependent sodium flux. Exposing neutrophils in vitro to a proinflammatory micromilieu with N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe, LPS, or IL-8 resulted in a diminished response regarding the increase in cellular size and pH. The detailed kinetics of the reduced reactivity of the neutrophil granulocytes could be illustrated in a near-real-time flow cytometric measurement. Last, the LPS-mediated impairment of the IL-8-induced response in neutrophils was confirmed in a translational, animal-free human whole blood model. Overall, we provide novel mechanistic insights for the interaction of IL-8 with neutrophil granulocytes and report in detail about its alteration during systemic inflammation.
Keywords: Flow cytometry; Interleukin 8; Intracellular pH; Lipopolysaccharide; Neutrophil granulocytes; Sodium-proton exchanger 1.
© 2021 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2003 Jan 9;348((2)):138–50. - PubMed
-
- Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Mar;13((3)):159–75. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M, Clark-Lewis I. Interleukin-8, a chemotactic and inflammatory cytokine. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 27;307((1)):97–101. - PubMed
-
- Alves-Filho JC, de Freitas A, Spiller F, Souto FO, Cunha FQ. The role of neutrophils in severe sepsis. Shock. 2008 Oct;30((Suppl 1)):3–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

