The diagnostic and prognostic value of H2AFY in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 33858382
- PMCID: PMC8051056
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08161-4
The diagnostic and prognostic value of H2AFY in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The potential correlation between H2AFY (also known as MacroH2A1) and the clinical characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients was analysed through gene expression profiles and clinical data in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, and the diagnostic and prognostic value of H2AFY in HCC was discussed.
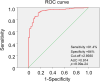
Methods: The gene expression data of HCC and the corresponding clinical characteristics of HCC patients were downloaded from the TCGA database. The differences in H2AFY in normal liver tissues and HCC were analysed. The relationship between H2AFY and clinical characteristics was analysed by Wilcoxon signed-rank test, logistic regression and Kruskal-Wallis test. The Kaplan-Meier method and the Cox regression method were used to analyse the relationship between overall survival and clinical characteristics of the patients. An ROC curve was used to predict the diagnostic value of H2AFY in HCC. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used to analyse the pathway enrichment of H2AFY.
Result: Compared with normal liver tissues, H2AFY was significantly highly expressed in HCC. H2AFY was positively correlated with the age, clinical stage, G stage (grade) and T stage (tumor stage) of liver cancer patients. Higher H2AFY expression predicted a poor prognosis in HCC patients. Cox regression analysis suggested that H2AFY was an independent risk factor for the prognosis of HCC patients. The ROC curve suggested that H2AFY had certain diagnostic value in HCC. GSEA suggested that H2AFY was correlated with lipid metabolism and a variety of tumour pathways.
Conclusion: Our study showed that H2AFY was significantly overexpressed in HCC. H2AFY may be a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for HCC, and high expression of H2AFY predicts a poor prognosis in patients with HCC.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; H2AFY; Hepatocellular carcinoma; MacroH2A1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Upregulation of Stress-Induced Protein Kinase CK1 Delta is associated with a Poor Prognosis for patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021 Jul;25(7):504-514. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2020.0093. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 34280005
-
Low expression of long noncoding RNA CTC-297N7.9 predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2019 Dec;8(18):7679-7692. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2618. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31674731 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Prognostic Value, Immune Implication and Biological Function of H2AFY Gene in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 24;12:723293. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.723293. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899687 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 May;24(10):5438-5445. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15258. Epub 2020 Apr 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32281724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential value and advances in research on bone mineral density (BMD) measurement in the auxiliary clinical assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Biosci Trends. 2024 Sep 16;18(4):398-403. doi: 10.5582/bst.2024.01235. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Biosci Trends. 2024. PMID: 39168610 Review.
Cited by
-
High expression of H2A histone family member Y promotes the proliferation and autophagy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):10654-10664. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2065761. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35472308 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with immune infiltration.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2503645. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2503645. Epub 2025 May 29. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40440122 Free PMC article.
-
The Histone Variant MacroH2A1 Impacts Circadian Gene Expression and Cell Phenotype in an In Vitro Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 20;9(8):1057. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081057. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440260 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Histone H2A Variants in Cancer Development, Prognosis, and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 9;25(6):3144. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063144. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MacroH2A Histone Variants in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 15;13(12):3003. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123003. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203934 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marrero JA, Feng Z, Wang Y, Nguyen MH, Befeler AS, Roberts LR, Reddy KR, Harnois D, Llovet JM, Normolle D, Dalhgren J, Chia D, Lok AS, Wagner PD, Srivastava S, Schwartz M. Alpha-fetoprotein, des-gamma carboxyprothrombin, and lectin-bound alpha-fetoprotein in early hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(1):110–118. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.04.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

