MicroRNAs as the critical regulators of Doxorubicin resistance in breast tumor cells
- PMID: 33858435
- PMCID: PMC8170947
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-01873-4
MicroRNAs as the critical regulators of Doxorubicin resistance in breast tumor cells
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatment options for breast cancer (BC) patients. However, about half of the BC patients are chemotherapeutic resistant. Doxorubicin (DOX) is considered as one of the first line drugs in the treatment of BC patients whose function is negatively affected by multi drug resistance. Due to the severe side effects of DOX, it is very important to diagnose the DOX resistant BC patients. Therefore, assessment of molecular mechanisms involved in DOX resistance can improve the clinical outcomes in BC patients by introducing the novel therapeutic and diagnostic molecular markers. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) as members of the non-coding RNAs family have pivotal roles in various cellular processes including cell proliferation and apoptosis. Therefore, aberrant miRNAs functions and expressions can be associated with tumor progression, metastasis, and drug resistance. Moreover, due to miRNAs stability in body fluids, they can be considered as non-invasive diagnostic markers for the DOX response in BC patients.
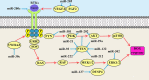
Main body: In the present review, we have summarized all of the miRNAs that have been reported to be associated with DOX resistance in BC for the first time in the world.
Conclusions: Since, DOX has severe side effects; it is required to distinguish the non DOX-responders from responders to improve the clinical outcomes of BC patients. This review highlights the miRNAs as pivotal regulators of DOX resistance in breast tumor cells. Moreover, the present review paves the way of introducing a non-invasive panel of prediction markers for DOX response among BC patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Chemo-resistance; Chemotherapy; Doxorubicin; MicroRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59(4):225–49. - PubMed
-
- Weigelt B, Reis-Filho JS. Histological and molecular types of breast cancer: is there a unifying taxonomy? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6(12):718. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

