KLF7/VPS35 axis contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression through CCDC85C-activated β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 33858520
- PMCID: PMC8048225
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-021-00585-6
KLF7/VPS35 axis contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression through CCDC85C-activated β-catenin pathway
Abstract
Objective: Dysregulation of KLF7 participates in the development of various cancers, but it is unclear whether there is a link between HCC and aberrant expression of KLF7. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of KLF7 in proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells.
Methods: CCK8, colony growth, transwell, cell cycle analysis and apoptosis detection were performed to explore the effect of KLF7, VPS35 and Ccdc85c on cell function in vitro. Xenografted tumor growth was used to assess in vivo role of KLF7. Chip-qPCR and luciferase reporter assays were applied to check whether KLF7 regulated VPS35 at transcriptional manner. Co-IP assay was performed to detect the interaction between VPS35 and Ccdc85c. Immunohistochemical staining and qRT-PCR analysis were performed in human HCC sampels to study the clinical significance of KLF7, VPS35 and β-catenin.
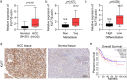
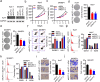
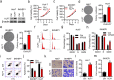
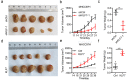
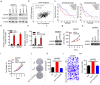
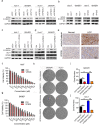
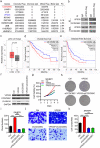
Results: Firstly, KLF7 was highly expressed in human HCC samples and correlated with patients' differentiation and metastasis status. KLF7 overexpression contributed to cell proliferation and invasion of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. KLF7 transcriptional activation of VPS35 was necessary for HCC tumor growth and metastasis. Further, co-IP studies revealed that VPS35 could interact with Ccdc85c in HCC cells. Rescue assay confirmed that overexpression of VPS35 and knockdown of Ccdc85c abolished the VPS35-medicated promotion effect on cell proliferation and invasion. Finally, KLF7/VPS35 axis regulated Ccdc85c, which involved in activation of β-catenin signaling pathway, confirmed using β-catenin inhibitor, GK974. Functional studies suggested that downregulation of Ccdc85c partly reversed the capacity of cell proliferation and invasion in HCC cells, which was regulated by VPS35 upregulation. Lastly, there was a positive correlation among KLF7, VPS35 and active-β-catenin in human HCC patients.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that KLF7/VPS35 axis promoted HCC cell progression by activating Ccdc85c-medicated β-catenin pathway. Targeting this signal axis might be a potential treatment strategy for HCC.
Keywords: Ccdc85c; Hepatocellular carcinoma; KLF7; LGK974; VPS35; Β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CCDC85C suppresses colorectal cancer cells proliferation and metastasis through activating GSK-3β and promoting β-catenin degradation.Cell Signal. 2023 Sep;109:110799. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110799. Epub 2023 Jul 9. Cell Signal. 2023. PMID: 37433398
-
GNA14 stimulation of KLF7 promotes malignant growth of endometrial cancer through upregulation of HAS2.BMC Cancer. 2021 Apr 23;21(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08202-y. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33892667 Free PMC article.
-
UNC119 promoted cell growth and migration by Wnt/β-catenin signal and TGF-β/EMT signal pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.J BUON. 2018 Nov-Dec;23(6):1717-1724. J BUON. 2018. PMID: 30610799
-
HMGB1-mediated elevation of KLF7 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis through upregulating TLR4 and PTK2.Theranostics. 2023 Jul 14;13(12):4042-4058. doi: 10.7150/thno.84388. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37554278 Free PMC article.
-
Metallothionein 1H (MT1H) functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2017 Feb 28;17(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3139-2. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28241806 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of Significant Modules and Targets of Xian-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction Based on the Analysis of Transcriptomics, Proteomics and Single-Cell Transcriptomics in Colorectal Tumor.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Mar 1;15:1483-1499. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S344861. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35256851 Free PMC article.
-
Promotion of colorectal cancer by transcription factor BHLHE40 involves upregulation of ADAM19 and KLF7.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 20;13:1122238. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1122238. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36890812 Free PMC article.
-
KLF7 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through Regulating SLC1A5-Mediated Tryptophan Metabolism.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Dec;28(23):e70245. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70245. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39648156 Free PMC article.
-
KLF7 enhances the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells via the miR-139-5p/TPD52 axis.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2385172. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2385172. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39097779 Free PMC article.
-
Stable and oscillatory hypoxia differentially regulate invasibility of breast cancer associated fibroblasts.Mechanobiol Med. 2024 Sep;2(3):100070. doi: 10.1016/j.mbm.2024.100070. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Mechanobiol Med. 2024. PMID: 40365532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Budny A, Kozlowski P, Kaminska M, Jankiewicz M, Kolak A, Budny B, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2017;43(255):133–139. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 201701D221176/Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (CN)
- 201901D111413/Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (CN)
- 201601032/Health and Family Planning Commission of Shanxi Province Scientific Research Project
- YB161705/Doctor Foundation of The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

