Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on anxiety and depression symptoms of young people in the global south: evidence from a four-country cohort study
- PMID: 33858874
- PMCID: PMC8053815
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049653
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on anxiety and depression symptoms of young people in the global south: evidence from a four-country cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To provide evidence on the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of young people who grew up in poverty in low/middle-income countries (LMICs).
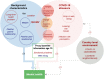
Design: A phone survey administered between August and October 2020 to participants of a population-based longitudinal cohort study established in 2002 comprising two cohorts born in 1994-1995 and 2001-2002 in Ethiopia, India (Andhra Pradesh and Telangana), Peru and Vietnam. We use logistic regressions to examine associations between mental health and pandemic-related stressors, structural factors (gender, age), and lifelong protective/risk factors (parent and peer relationship, wealth, long-term health problems, past emotional problems, subjective well-being) measured at younger ages.
Setting: A geographically diverse, poverty-focused sample, also reaching those without mobile phones or internet access.
Participants: 10 496 individuals were approached; 9730 participated. Overall, 8988 individuals were included in this study; 4610 (51%) men and 4378 (49%) women. Non-inclusion was due to non-location or missing data.
Main outcome measures: Symptoms consistent with at least mild anxiety or depression were measured by Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (≥5) or Patient Health Questionnaire-8 (≥5).
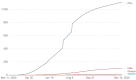
Results: Rates of symptoms of at least mild anxiety (depression) were highest in Peru at 41% (32%) (95% CI 38.63% to 43.12%; (29.49-33.74)), and lowest in Vietnam at 9% (9%) (95% CI 8.16% to 10.58%; (8.33-10.77)), mirroring COVID-19 mortality rates. Women were most affected in all countries except Ethiopia. Pandemic-related stressors such as health risks/expenses, economic adversity, food insecurity, and educational or employment disruption were risk factors for anxiety and depression, though showed varying levels of importance across countries. Prior parent/peer relationships were protective factors, while long-term health or emotional problems were risk factors.
Conclusion: Pandemic-related health, economic and social stress present significant risks to the mental health of young people in LMICs where mental health support is limited, but urgently needed to prevent long-term consequences.
Keywords: COVID-19; anxiety disorders; depression & mood disorders.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CP, MF, AH, DS, ASJ, RE, TW and LTD report grants from the FCDO, during the conduct of the study.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Substantial investment needed to avert mental health crisis, 2020. Available: https://www.who.int/news/item/14-05-2020-substantial-investment-needed-t... [Accessed 14 May 2020].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
