Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals following mRNA vaccination
- PMID: 33858945
- PMCID: PMC8158969
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abi6950
Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals following mRNA vaccination
Abstract
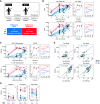
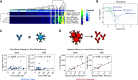
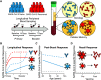
Novel mRNA vaccines for SARS-CoV-2 have been authorized for emergency use. Despite their efficacy in clinical trials, data on mRNA vaccine-induced immune responses are mostly limited to serological analyses. Here, we interrogated antibody and antigen-specific memory B cells over time in 33 SARS-CoV-2 naïve and 11 SARS-CoV-2 recovered subjects. SARS-CoV-2 naïve individuals required both vaccine doses for optimal increases in antibodies, particularly for neutralizing titers against the B.1.351 variant. Memory B cells specific for full-length spike protein and the spike receptor binding domain (RBD) were also efficiently primed by mRNA vaccination and detectable in all SARS-CoV-2 naive subjects after the second vaccine dose, though the memory B cell response declined slightly with age. In SARS-CoV-2 recovered individuals, antibody and memory B cell responses were significantly boosted after the first vaccine dose; however, there was no increase in circulating antibodies, neutralizing titers, or antigen-specific memory B cells after the second dose. This robust boosting after the first vaccine dose strongly correlated with levels of pre-existing memory B cells in recovered individuals, identifying a key role for memory B cells in mounting recall responses to SARS-CoV-2 antigens. Together, our data demonstrated robust serological and cellular priming by mRNA vaccines and revealed distinct responses based on prior SARS-CoV-2 exposure, whereby COVID-19 recovered subjects may only require a single vaccine dose to achieve peak antibody and memory B cell responses. These findings also highlight the utility of defining cellular responses in addition to serologies and may inform SARS-CoV-2 vaccine distribution in a resource-limited setting.
Copyright © 2021, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


Update of
-
Longitudinal Analysis Reveals Distinct Antibody and Memory B Cell Responses in SARS-CoV2 Naïve and Recovered Individuals Following mRNA Vaccination.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Mar 6:2021.03.03.21252872. doi: 10.1101/2021.03.03.21252872. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: Sci Immunol. 2021 Apr 15;6(58):eabi6950. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abi6950. PMID: 33688691 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- COVID-19 Map - Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center , (available at https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html).
-
- Polack F. P., Thomas S. J., Kitchin N., Absalon J., Gurtman A., Lockhart S., Perez J. L., Pérez Marc G., Moreira E. D., Zerbini C., Bailey R., Swanson K. A., Roychoudhury S., Koury K., Li P., Kalina W. V., Cooper D., Frenck R. W. Jr., Hammitt L. L., Türeci Ö., Nell H., Schaefer A., Ünal S., Tresnan D. B., Mather S., Dormitzer P. R., Şahin U., Jansen K. U., Gruber W. C.; C4591001 Clinical Trial Group , Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2603–2615 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Widge A. T., Rouphael N. G., Jackson L. A., Anderson E. J., Roberts P. C., Makhene M., Chappell J. D., Denison M. R., Stevens L. J., Pruijssers A. J., McDermott A. B., Flach B., Lin B. C., Doria-Rose N. A., O’Dell S., Schmidt S. D., Neuzil K. M., Bennett H., Leav B., Makowski M., Albert J., Cross K., Edara V.-V., Floyd K., Suthar M. S., Buchanan W., Luke C. J., Ledgerwood J. E., Mascola J. R., Graham B. S., Beigel J. H.; mRNA-1273 Study Group , Durability of Responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 80–82 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI152236/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI082630/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- AI149680/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI152236/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082630/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R38 HL143613/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI108545/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI105343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR076951-01/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI055400/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI105343/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- AI108545/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HL143613/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR076951/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI070077/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI155577/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI155577/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI149680/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI0450080/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

