Meta-analysis of HIV-1 vaccine elicited mucosal antibodies in humans
- PMID: 33859204
- PMCID: PMC8050318
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-021-00305-8
Meta-analysis of HIV-1 vaccine elicited mucosal antibodies in humans
Abstract
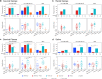
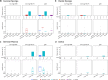
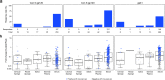
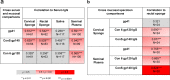
We studied mucosal immune responses in six HIV-1 vaccine trials investigating different envelope (Env)-containing immunogens. Regimens were classified into four categories: DNA/vector, DNA/vector plus protein, protein alone, and vector alone. We measured HIV-1-specific IgG and IgA in secretions from cervical (n = 111) and rectal swabs (n = 154), saliva (n = 141), and seminal plasma (n = 124) and compared to corresponding blood levels. Protein-containing regimens had up to 100% response rates and the highest Env-specific IgG response rates. DNA/vector groups elicited mucosal Env-specific IgG response rates of up to 67% that varied across specimen types. Little to no mucosal IgA responses were observed. Overall, gp41- and gp140-specific antibodies dominated gp120 mucosal responses. In one trial, prior vaccination with a protein-containing immunogen maintained durability of cervical and rectal IgG for up to 17 years. Mucosal IgG responses were boosted after revaccination. These findings highlight a role for protein immunization in eliciting HIV-1-specific mucosal antibodies and the ability of HIV-1 vaccines to elicit durable HIV-1-specific mucosal IgG.
Conflict of interest statement
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. Potential competing interests: Co-authors M.A.A. and L.P. are employed by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), sponsor of the clinical trials described in this manuscript. All authors are recipients of NIAID funding, and this publication is a result of activities funded by the NIAID. M.A. and L.P. are not involved with the process of funding these awards nor in their administration of scientific aspects and, in accordance with NIAID policies, are deferred from decisions regarding the funding of coauthors for a requisite period. Co-author HLR is a co-founder and employee of GeoVax Lab, Inc. and owns stocks in GeoVax Lab, Inc, and is an inventor on U.S. Patents 7,795,017, 8,623,379, 7,867,982, and 9,453,239 addressing D.N.A. and M.V.A. immunogens being developed for a Clade B HIV vaccine. Co-authors K.E.S., A.D., X.H., S.S.L., A.C., J.H., A.D., X.S., S.S., N.L.Y., P.S., G.C., P.A.G., J.M., G.G., G.P., S.G., A.K.R., Y.H., C.M., N.G., S.K., P.B.G., M.J.M., Y.H., and G.D.T. declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

