Boosting the signal-to-noise of low-field MRI with deep learning image reconstruction
- PMID: 33859218
- PMCID: PMC8050246
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-87482-7
Boosting the signal-to-noise of low-field MRI with deep learning image reconstruction
Abstract
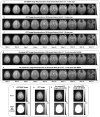
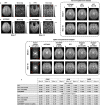
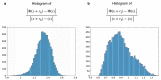
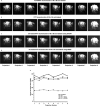
Recent years have seen a resurgence of interest in inexpensive low magnetic field (< 0.3 T) MRI systems mainly due to advances in magnet, coil and gradient set designs. Most of these advances have focused on improving hardware and signal acquisition strategies, and far less on the use of advanced image reconstruction methods to improve attainable image quality at low field. We describe here the use of our end-to-end deep neural network approach (AUTOMAP) to improve the image quality of highly noise-corrupted low-field MRI data. We compare the performance of this approach to two additional state-of-the-art denoising pipelines. We find that AUTOMAP improves image reconstruction of data acquired on two very different low-field MRI systems: human brain data acquired at 6.5 mT, and plant root data acquired at 47 mT, demonstrating SNR gains above Fourier reconstruction by factors of 1.5- to 4.5-fold, and 3-fold, respectively. In these applications, AUTOMAP outperformed two different contemporary image-based denoising algorithms, and suppressed noise-like spike artifacts in the reconstructed images. The impact of domain-specific training corpora on the reconstruction performance is discussed. The AUTOMAP approach to image reconstruction will enable significant image quality improvements at low-field, especially in highly noise-corrupted environments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

