TNF-α impairs EP4 signaling through the association of TRAF2-GRK2 in primary fibroblast-like synoviocytes
- PMID: 33859345
- PMCID: PMC8791952
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-021-00654-z
TNF-α impairs EP4 signaling through the association of TRAF2-GRK2 in primary fibroblast-like synoviocytes
Abstract
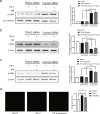
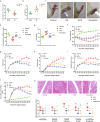
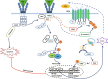
Our previous study showed that chronic treatment with tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) decreased cAMP concentration in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rats. In this study we investigated how TNF-α impairs cAMP homeostasis, particularly clarifying the potential downstream molecules of TNF-α and prostaglandin receptor 4 (EP4) signaling that would interact with each other. Using a cAMP FRET biosensor PM-ICUE3, we demonstrated that TNF-α (20 ng/mL) blocked ONO-4819-triggered EP4 signaling, but not Butaprost-triggered EP2 signaling in normal rat FLSs. We showed that TNF-α (0.02-20 ng/mL) dose-dependently reduced EP4 membrane distribution in normal rat FLS. TNF-α significantly increased TNF receptor 2 (TNFR2) expression and stimulated proliferation in human FLS (hFLS) via ecruiting TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) to cell membrane. More interestingly, we revealed that TRAF2 interacted with G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK2) in the cytoplasm of primary hFLS and helped to bring GRK2 to cell membrane in response of TNF-α stimulation, the complex of TRAF2 and GRK2 then separated on the membrane, and translocated GRK2 induced the desensitization and internalization of EP4, leading to reduced production of intracellular cAMP. Silencing of TRAF2 by siRNA substantially diminished TRAF2-GRK2 interaction, blocked the translocation of GRK2, and resulted in upregulated expression of membrane EP4 and intracellular cAMP. In CIA rats, administration of paroxetine to inhibit GRK2 effectively improved the symptoms and clinic parameters with significantly reduced joint synovium inflammation and bone destruction. These results elucidate a novel form of cross-talk between TNFR (a cytokine receptor) and EP4 (a typical G protein-coupled receptor) signaling pathways. The interaction between TRAF2 and GRK2 may become a potential new drug target for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: EP4; GRK2; TNFR2; TRAF2; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CPS and SIMM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Jia XY, Chang Y, Sun XJ, Dai X, Wei W. The role of prostaglandin E2 receptor signaling of dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;23:163–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

