Compressed sensing for highly efficient imaging transcriptomics
- PMID: 33859401
- PMCID: PMC8355028
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-021-00883-x
Compressed sensing for highly efficient imaging transcriptomics
Abstract
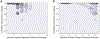
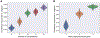
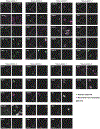
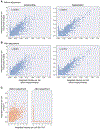
Recent methods for spatial imaging of tissue samples can identify up to ~100 individual proteins1-3 or RNAs4-10 at single-cell resolution. However, the number of proteins or genes that can be studied in these approaches is limited by long imaging times. Here we introduce Composite In Situ Imaging (CISI), a method that leverages structure in gene expression across both cells and tissues to limit the number of imaging cycles needed to obtain spatially resolved gene expression maps. CISI defines gene modules that can be detected using composite measurements from imaging probes for subsets of genes. The data are then decompressed to recover expression values for individual genes. CISI further reduces imaging time by not relying on spot-level resolution, enabling lower magnification acquisition, and is overall about 500-fold more efficient than current methods. Applying CISI to 12 mouse brain sections, we accurately recovered the spatial abundance of 37 individual genes from 11 composite measurements covering 180 mm2 and 476,276 cells.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Comment in
-
Accelerating imaging transcriptomics.Nat Methods. 2021 Jun;18(6):594. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01189-1. Nat Methods. 2021. PMID: 34099935 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

