New diagnostic algorithm for detection of covert Bow Hunter's Syndrome
- PMID: 33859523
- PMCID: PMC8040409
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.56442
New diagnostic algorithm for detection of covert Bow Hunter's Syndrome
Abstract
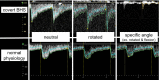
Bow hunter's syndrome (BHS) should not be overlooked as a cause of cerebral infarction in the posterior circulation. However, covert BHS, which does not impair blood flow with simple rotation but only at certain angles, may make the diagnosis of BHS difficult. We propose a new algorithm to detect BHS or covert BHS. We recommend that BHS and covert BHS be detected by noninvasive duplex ultrasonography, which will allow for appropriate treatment.
Keywords: algorithm; bow hunter's syndrome; covert bow hunter's syndrome; diagnosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Kimihira L, Yoshimoto T, Saito S. et al. Various head rotations for ultrasonographic diagnosis of bilateral bow hunter's syndrome. Acta Neurol Belg. 2020;120:1003–1005. - PubMed
-
- Jost GF, Dailey AT. Bow hunter's syndrome revisited: 2 new cases and literature review of 124 cases. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;38:E7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

