Para-chloro-2-[18F]fluoroethyl-etomidate: A promising new PET radiotracer for adrenocortical imaging
- PMID: 33859526
- PMCID: PMC8040415
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.51206
Para-chloro-2-[18F]fluoroethyl-etomidate: A promising new PET radiotracer for adrenocortical imaging
Abstract
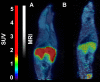
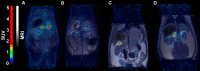
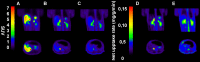
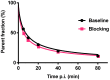
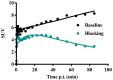
Introduction: [11C]Metomidate ([11C]MTO), the methyl ester analogue of etomidate, was developed as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer for adrenocortical tumours and has also been suggested for imaging in primary aldosteronism (PA). A disadvantage of [11C]MTO is the rather high non-specific binding in the liver, which impacts both visualization and quantification of the uptake in the right adrenal gland. Furthermore, the short 20-minute half-life of carbon-11 is a logistic challenge in the clinical setting. Objectives: The aim of this study was to further evaluate the previously published fluorine-18 (T1/2=109.5 min) etomidate analogue, para-chloro-2-[18F]fluoroethyl etomidate; [18F]CETO, as an adrenal PET tracer. Methods: In vitro experiments included autoradiography on human and cynomolgus monkey (non-human primate, NHP) tissues and binding studies on adrenal tissue from NHPs. In vivo studies with [18F]CETO in mice, rats and NHP, using PET and CT/MRI, assessed biodistribution and binding specificity in comparison to [11C]MTO. Results: The binding of [18F]CETO in the normal adrenal cortex, as well as in human adrenocortical adenomas and adrenocortical carcinomas, was shown to be specific, both in vitro (in humans) and in vivo (in rats and NHP) with an in vitro Kd of 0.66 nM. Non-specific uptake of [18F]CETO in NHP liver was found to be low compared to that of [11C]MTO. Conclusions: High specificity of [18F]CETO to the adrenal cortex was demonstrated, with in vivo binding properties qualitatively surpassing those of [11C]MTO. Non-specific binding to the liver was significantly lower than that of [11C]MTO. [18F]CETO is a promising new PET tracer for imaging of adrenocortical disease and should be evaluated further in humans.
Keywords: 18F-CETO; Adrenal masses; Adrenal tracer; Positron emission tomography; Primary aldosteronism.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

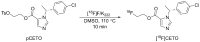





Comment in
-
First-in-human evaluation of [18F]CETO: a novel tracer for adrenocortical tumours.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Jan;50(2):398-409. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05957-9. Epub 2022 Sep 8. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36074157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan ST, Sundin A, Juhlin C, Långström B, Bergström M, Eriksson B. 11C-metomidate PET imaging of adrenocortical cancer. Eur J Nucl Med. 2002. p: 403-10. - PubMed
-
- Radu M. Non-adrenal tumours encountered during adrenal surgery. Society for Endocrinology BES 2019. Brighton, UK: Endocrine Abstracts. 2019.
-
- Mitterhauser M, Dobrozemsky G, Zettinig G, Wadsak W, Vierhapper H, Dudczak R. et al. Imaging of adrenocortical metastases with [11C]metomidate. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006;33:974. - PubMed
-
- O´Shea PM, O´Donoghue D, Bashari W, Senanyake R, Joyce MB, Powlson AS, 11C-Metomidate PET/CT is a useful adjunct for lateralization of primary aldosteronism in routine clinical practice. Clinical Endocrinology. 2019. p: 670-9. - PubMed
-
- Karashima S, Kometani M, Tsujiguchi H, Asakura H, Nakano S, Usukura M. et al. Prevalence of primary aldosteronism without hypertension in the general population: Results in Shika study. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension. 2018;40:118–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

