Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles, Virulence Genes, and Genetic Diversity of Thermophilic Campylobacter Species Isolated From a Layer Poultry Farm in Korea
- PMID: 33859624
- PMCID: PMC8043113
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.622275
Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles, Virulence Genes, and Genetic Diversity of Thermophilic Campylobacter Species Isolated From a Layer Poultry Farm in Korea
Abstract
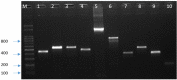
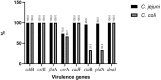
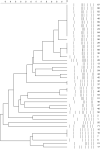
Thermophilic Campylobacter species are among the major etiologies of bacterial enteritis globally. This study aimed at assessing the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) profiles, virulence genes, and genetic diversity of thermophilic Campylobacter species isolated from a layer poultry farm in South Korea. One hundred fifty-three chicken feces were collected from two layer poultry farms in Gangneung, South Korea. The Campylobacter species were isolated by cultural techniques, while PCR and sequencing were used for species confirmation. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing for six antimicrobials [ciprofloxacin (CIP), nalidixic acid (NAL), sitafloxacin (SIT), erythromycin (ERY), tetracycline (TET), and gentamicin (GEN)] was carried out by broth microdilution. Three AMR and nine virulence genes were screened by PCR. Genotyping was performed by flaA-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and multilocus sequence typing (MLST). Of the 153 samples, Campylobacter spp. were detected in 55 (35.9%), with Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli being 49 (89.1%) and six (10.9%), respectively. High-level resistance was observed for CIP (100%), NAL (100%), and TET (C. jejuni, 93.9%; C. coli: 83.3%). No resistance was observed for SIT. The missense mutation (C257T) in gyrA gene was confirmed by sequencing, while the tet(O) gene was similar to known sequences in GenBank. The rate of multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains was 8.2%, and they all belonged to C. jejuni. All Campylobacter isolates possessed five virulence genes (cdtB, cstII, flaA, cadF, and dnaJ), but none possessed ggt, while the rates for other genes (csrA, ciaB, and pldA) ranged between 33.3 and 95.9%. The flaA-RFLP yielded 26 flaA types (C. jejuni: 21 and C. coli: five), while the MLST showed 10 sequence types (STs) for C. jejuni and three STs for C. coli, with CC-607 (STs 3611) and CC-460 (ST-460) being predominant. Among the 10 STs of C. jejuni, three were newly assigned. The findings of this study highlight the increased resistance to quinolones and TET, the virulence potential, and the diverse genotypes among Campylobacter strains isolated from the layer poultry farm.
Keywords: Campylobacter; Korea; antimicrobial resistance; flaA RFLP; multilocus sequence typing; poultry; quinolones.
Copyright © 2021 Gahamanyi, Song, Yoon, Mboera, Matee, Mutangana, Amachawadi, Komba and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Campylobacter spp. isolated from poultry in Iran: Antibiotic resistance profiles, virulence genes, and molecular mechanisms.Food Sci Nutr. 2022 Nov 21;11(2):1142-1153. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3152. eCollection 2023 Feb. Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36789060 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Characterization of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Thermophilic Campylobacter Strains Isolated from Layer Chicken Feces in Gangneung, South Korea by Whole-Genome Sequencing.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 25;12(8):1131. doi: 10.3390/genes12081131. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440305 Free PMC article.
-
Short Variable Regions flaA Gene (SVR-flaA) Diversity and Virulence Profile of Multidrug-Resistant Campylobacter from Poultry and Poultry Meat in India.J Food Prot. 2024 Jul;87(7):100308. doi: 10.1016/j.jfp.2024.100308. Epub 2024 May 28. J Food Prot. 2024. PMID: 38815809
-
Distribution of virulence and antibiotic resistance genes in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from broiler chickens in Tunisia.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2022 Dec;55(6 Pt 2):1273-1282. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Jul 17. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2022. PMID: 34340908 Review.
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli over time in Thailand under a One Health approach: A systematic review and meta-analysis.One Health. 2025 Jan 10;20:100965. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2025.100965. eCollection 2025 Jun. One Health. 2025. PMID: 39898318 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pan-Genome Analysis of Campylobacter: Insights on the Genomic Diversity and Virulence Profile.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0102922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01029-22. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36069574 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of antibiotic resistant Campylobacter among patients attending clinical settings in Kigali, Rwanda.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 15;25(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10626-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39955487 Free PMC article.
-
Trends, clinical characteristics, antimicrobial susceptibility patterns, and outcomes of Campylobacter bacteraemia: a multicentre retrospective study.Infection. 2024 Jun;52(3):857-864. doi: 10.1007/s15010-023-02118-4. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Infection. 2024. PMID: 37910310
-
A Decade of Antimicrobial Resistance in Human and Animal Campylobacter spp. Isolates.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;13(9):904. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090904. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance in Campylobacter spp. Livestock Isolates.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;12(2):402. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020402. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830312 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham S., Sahibzada S., Hewson K., Laird T., Abraham R., Pavic A., et al. (2020). Emergence of fluoroquinolone-resistant Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli among Australian chickens in the absence of fluoroquinolone use. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 86:e02765-19. 10.1128/AEM.02765-19 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alaboudi A. R., Malkawi I. M., Osaili T. M., Abu-Basha E. A., Guitian J. (2020). Prevalence, antibiotic resistance and genotypes of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from chickens in Irbid governorate, Jordan. Intern. J. Food Microbiol. 327:108656. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108656 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Edany A. A., Khudor M. H., Radhi L. Y. (2015). Isolation, identification and toxigenic aspects of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from slaughtered cattle and sheep at Basrah city. Microbiology 14 316–327.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

