Epigenetic Modifiers: Anti-Neoplastic Drugs With Immunomodulating Potential
- PMID: 33859645
- PMCID: PMC8042276
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.652160
Epigenetic Modifiers: Anti-Neoplastic Drugs With Immunomodulating Potential
Abstract
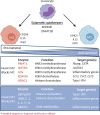
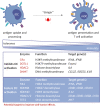
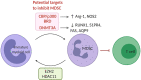
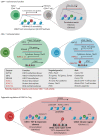
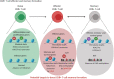
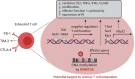
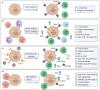
Cancer cells are under the surveillance of the host immune system. Nevertheless, a number of immunosuppressive mechanisms allow tumors to escape protective responses and impose immune tolerance. Epigenetic alterations are central to cancer cell biology and cancer immune evasion. Accordingly, epigenetic modulating agents (EMAs) are being exploited as anti-neoplastic and immunomodulatory agents to restore immunological fitness. By simultaneously acting on cancer cells, e.g. by changing expression of tumor antigens, immune checkpoints, chemokines or innate defense pathways, and on immune cells, e.g. by remodeling the tumor stroma or enhancing effector cell functionality, EMAs can indeed overcome peripheral tolerance to transformed cells. Therefore, combinations of EMAs with chemo- or immunotherapy have become interesting strategies to fight cancer. Here we review several examples of epigenetic changes critical for immune cell functions and tumor-immune evasion and of the use of EMAs in promoting anti-tumor immunity. Finally, we provide our perspective on how EMAs could represent a game changer for combinatorial therapies and the clinical management of cancer.
Keywords: cancer; epigenetics; immune evasion; immunotherapy; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2021 Maes, Mondino, Lasarte, Agirre, Vanderkerken, Prosper and Breckpot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer Epigenetics, Tumor Immunity, and Immunotherapy.Trends Cancer. 2020 Jul;6(7):580-592. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.02.003. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Trends Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32610068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB in the New Era of Cancer Therapy.Trends Cancer. 2020 Aug;6(8):677-687. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 May 11. Trends Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32409139 Review.
-
Fueling the Revolution: Targeting Metabolism to Enhance Immunotherapy.Cancer Immunol Res. 2021 Mar;9(3):255-260. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-20-0791. Cancer Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33648947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Turning Cold into Hot: Firing up the Tumor Microenvironment.Trends Cancer. 2020 Jul;6(7):605-618. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.02.022. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Trends Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32610070 Review.
-
HLA-G/LILRBs: A Cancer Immunotherapy Challenge.Trends Cancer. 2021 May;7(5):389-392. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2021.01.004. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Trends Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33563576
Cited by
-
The Achilles' heel of cancer survivors: fundamentals of accelerated cellular senescence.J Clin Invest. 2022 Jul 1;132(13):e158452. doi: 10.1172/JCI158452. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35775492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDLIM2: Signaling pathways and functions in cancer suppression and host immunity.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Dec;1876(2):188630. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188630. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34571051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current State of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Cancer-Immunity Cycle: Therapeutic Relevance and Overcoming Clinical Limitations Using Hydrogels.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Mar;10(8):e2205803. doi: 10.1002/advs.202205803. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36670068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interrogating Epigenome toward Personalized Approach in Cutaneous Melanoma.J Pers Med. 2021 Sep 9;11(9):901. doi: 10.3390/jpm11090901. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34575678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current understanding of epigenetics role in melanoma treatment and resistance.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Oct 12;22(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02738-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36224606 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

