Role of serotonin receptor signaling in cancer cells and anti-tumor immunity
- PMID: 33859748
- PMCID: PMC8039959
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.55986
Role of serotonin receptor signaling in cancer cells and anti-tumor immunity
Abstract
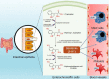
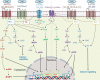
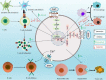
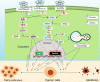
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a neurotransmitter known to affect emotion, behavior, and cognition, and its effects are mostly studied in neurological diseases. The crosstalk between the immune cells and the nervous system through serotonin and its receptors (5-HTRs) in the tumor microenvironment and the secondary lymphoid organs are known to affect cancer pathogenesis. However, the molecular mechanism of - alteration in the phenotype and function of - innate and adaptive immune cells by serotonin is not well explored. In this review, we discuss how serotonin and serotonin receptors modulate the phenotype and function of various immune cells, and how the 5-HT-5-HTR axis modulates antitumor immunity. Understanding how 5-HT and immune signaling are involved in tumor immunity could help improve therapeutic strategies to control cancer progression and metastasis.
Keywords: 5-hydroxytryptamine; neuroimmune communication; neurotransmitter; serotonergic system; serotonin receptor.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Walther DJ, Peter JU, Bashammakh S, Hörtnagl H, Voits M, Fink H. et al. Synthesis of serotonin by a second tryptophan hydroxylase isoform. Science. 2003;299:1078197. - PubMed
-
- Mondanelli G, Volpi C. The double life of serotonin metabolites: in the mood for joining neuronal and immune systems. Curr Opin Immunol. 2020;70:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Veenstra-VanderWeele J, Anderson GM, Cook EH Jr. Pharmacogenetics and the serotonin system: initial studies and future directions. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;410:165–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

