Harnessing the tunable cavity of nanoceria for enhancing Y-27632-mediated alleviation of ocular hypertension
- PMID: 33859757
- PMCID: PMC8039939
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.54525
Harnessing the tunable cavity of nanoceria for enhancing Y-27632-mediated alleviation of ocular hypertension
Abstract
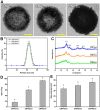
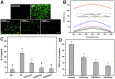
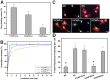
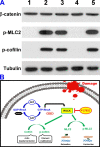
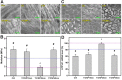
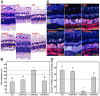
Background: Y-27632 is a potent ophthalmic drug for the treatment of ocular hypertension, a globally prevalent eye disease. However, the sustained delivery of Y-27632 by a therapeutic carrier to lesion sites located in the inner segments of the eye for effectively treating the ocular disorder still remains challenging. Methods: To realize the goal, a strategy based on solvothermal-assisted deposition/infiltration in combination with surface modification is utilized to synthesize hollow mesoporous ceria nanoparticles (HMCNs) with tailorable shell thicknesses and drug release profiles. The shell thickness of HMCNs is rationally exploited for achieving sustained drug release and advanced therapeutic benefits. Results: The shell thickness can regulate release profiles of Y-27632, displaying that thick and thin (~40 nm and ~10 nm) shelled HMCNs reveal burst release characteristics (within 2 days) or limited drug loading content (~10% for the 40 nm thick). As a compromise, the HMCNs with moderate shell thickness (~20 nm) possess the most sustained drug release over a period of 10 days. In a rabbit model of glaucoma, a single instillation of the optimized Y-27632-loaded HMCNs can effectively treat glaucoma for 10 days via simultaneously repairing the defected cornea (recovery of ~93% ATP1A1 mRNA levels), restoring the reduced thickness of outer nuclear layer to normal (~64 µm), and restoring ~86% of the impaired photoreceptor cells. Conclusion: A comprehensive study on the importance of HMCN shell thickness in developing long-acting nano eye drops for the efficient management of glaucoma is proposed. The findings suggest a central role of nanobiomaterial structural engineering in developing the long-life eye drops for pharmacological treatment of intraocular diseases.
Keywords: Y-27632; ceria nanostructure; hollow carrier system; ocular therapeutics; shell thickness.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T, Cheng CY. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:2081–2090. - PubMed
-
- Zhang K, Zhang L, Weinreb RN. Ophthalmic drug discovery: novel targets and mechanisms for retinal diseases and glaucoma. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2012;11:541–559. - PubMed
-
- Kotecha A. What biomechanical properties of the cornea are relevant for the clinician? Surv Ophthalmol. 2007;52:S109–S114. - PubMed
-
- Wiederholt M, Thieme H, Stumpff F. The regulation of trabecular meshwork and ciliary muscle contractility. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2000;19:271–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

