Causes of Death After Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 33859947
- PMCID: PMC8042257
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.647179
Causes of Death After Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
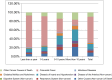
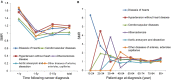
Background: Non-cancer causes of death in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) have not received much attention until now. The purpose of the current study is to investigate the non-cancer causes of death in patients with CRC at different periods of latency. Methods: Eligible patients with CRC were included from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, and standardized mortality ratios (SMRs) were calculated using the SEER*Stat software 8.3.8. Results: A total of 475,771 patients with CRC were included, of whom 230,841 patients died during the follow-up period. Within 5 years, CRC was the leading cause of death. Over time, non-cancer causes of death account for an increasing proportion. When followed up for more than 10 years, non-cancer deaths accounted for 71.9% of all deaths worldwide. Cardiovascular diseases were the most common causes of non-cancer deaths, accounting for 15.4% of the total mortality. Patients had a significantly higher risk of death from septicemia within the first year after diagnosis compared with the general population (SMR, 3.39; 95% CI, 3.11-3.69). Within 5-10 years after CRC diagnosis, patients had a significantly higher risk of death from diabetes mellitus (SMR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.19-1.36). During the course of more than 10 years, patients with CRC had a significantly higher risk of death from atherosclerosis (SMR 1.47; 95% CI, 1.11-1.9). Conclusions: Although CRC has always been the leading cause of death in patients with CRC, non-cancer causes of death should not be ignored. For patients with cancer, we should not only focus on anti-tumor therapies but also pay attention to the occurrence of other risks to prevent and manage them in advance.
Keywords: and End Results database; cardiovascular disease; colorectal cancer; epidemiology; non-cancer deaths; standardized mortality ratios; surveillance.
Copyright © 2021 Feng, Jin, Guo, Wasan, Ruan and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources