Ultrasound-Responsive Nanocarriers in Cancer Treatment: A Review
- PMID: 33860189
- PMCID: PMC8033618
- DOI: 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00212
Ultrasound-Responsive Nanocarriers in Cancer Treatment: A Review
Abstract
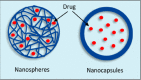
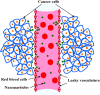
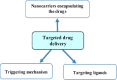
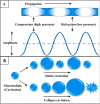
The safe and effective delivery of anticancer agents to diseased tissues is one of the significant challenges in cancer therapy. Conventional anticancer agents are generally cytotoxins with poor pharmacokinetics and bioavailability. Nanocarriers are nanosized particles designed for the selectivity of anticancer drugs and gene transport to tumors. They are small enough to extravasate into solid tumors, where they slowly release their therapeutic load by passive leakage or biodegradation. Using smart nanocarriers, the rate of release of the entrapped therapeutic(s) can be increased, and greater exposure of the tumor cells to the therapeutics can be achieved when the nanocarriers are exposed to certain internally (enzymes, pH, and temperature) or externally (light, magnetic field, and ultrasound) applied stimuli that trigger the release of their load in a safe and controlled manner, spatially and temporally. This review gives a comprehensive overview of recent research findings on the different types of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers and their application in cancer treatment with a particular focus on ultrasound.
© 2021 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

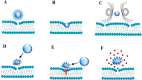
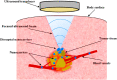
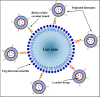

References
-
- Cancer Research UK . Worldwide cancer statistics. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/w... (accessed September 8, 2020).
-
- Kaplun A. P.; Bezrukov D. A.; Shvets V. I. (2011) Rational Design of Nano- and Micro-Size Medicinal Forms of Biologically Active Substances. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 47 (8), 711–717. 10.1134/S0003683811080072. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
