Proadrenomedullin N-Terminal 20 Peptides (PAMPs) Are Agonists of the Chemokine Scavenger Receptor ACKR3/CXCR7
- PMID: 33860204
- PMCID: PMC8033753
- DOI: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00006
Proadrenomedullin N-Terminal 20 Peptides (PAMPs) Are Agonists of the Chemokine Scavenger Receptor ACKR3/CXCR7
Abstract
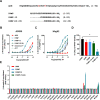
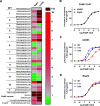
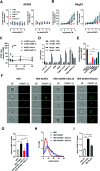
Adrenomedullin (ADM) and proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP) are two peptides with vasodilative, bronchodilative, and angiogenic properties, originating from a common precursor, proADM. Previous studies proposed that the atypical chemokine receptor ACKR3 might act as a low-affinity scavenger for ADM, regulating its availability for its cognate receptor calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR) in complex with a receptor activity modifying protein (RAMP). In this study, we compared the activation of ACKR3 by ADM and PAMP, as well as other related members of the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) family. Irrespective of the presence of RAMPs, ADM was the only member of the CGRP family to show moderate activity toward ACKR3. Remarkably, PAMP, and especially further processed PAMP-12, had a stronger potency toward ACKR3 than ADM. Importantly, PAMP-12 induced β-arrestin recruitment and was efficiently internalized by ACKR3 without inducing G protein or ERK signaling in vitro. Our results further extend the panel of endogenous ACKR3 ligands and broaden ACKR3 functions to a regulator of PAMP-12 availability for its primary receptor Mas-related G-protein-coupled receptor member X2 (MrgX2).
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reassessing the adrenomedullin scavenging function of ACKR3 in lymphatic endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2023 May 30;18(5):e0285597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285597. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37252916 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus 8-encoded chemokine vCCL2/vMIP-II is an agonist of the atypical chemokine receptor ACKR3/CXCR7.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 15;114:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 May 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27238288
-
Mutational analysis of the extracellular disulphide bridges of the atypical chemokine receptor ACKR3/CXCR7 uncovers multiple binding and activation modes for its chemokine and endogenous non-chemokine agonists.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;153:299-309. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.03.007. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29530506
-
Proadrenomedullin-derived peptides in the paracrine control of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis.Int Rev Cytol. 2001;206:249-84. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(01)06024-7. Int Rev Cytol. 2001. PMID: 11407762 Review.
-
Regulation of adrenomedullin and its family peptide by RAMP system--lessons from genetically engineered mice.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2013 Aug;14(5):347-57. doi: 10.2174/13892037113149990052. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2013. PMID: 23745699 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Potential of Adrenomedullin Signaling in the Cardiovascular System.Circ Res. 2023 Apr 28;132(9):1185-1202. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.321673. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37104556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical chemokine receptors in the immune system.Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Oct;24(10):753-769. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01025-5. Epub 2024 May 7. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38714818 Review.
-
Design, Synthesis and Pharmacological Characterization of the First Photoswitchable Small-Molecule Agonist for the Atypical Chemokine Receptor 3.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 18;10(8):8675-8686. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11583. eCollection 2025 Mar 4. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40060784 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic Activation of ACKR3 Signaling Regulates Lymphatic Response After Ischemic Heart Injury.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025 May;45(5):754-768. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.322288. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025. PMID: 40143814
-
Serial single-cell RNA sequencing unveils drug resistance and metastatic traits in stage IV breast cancer.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 Oct 3;8(1):222. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00723-6. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39363009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachelerie F.; Ben-Baruch A.; Burkhardt A. M.; Combadiere C.; Farber J. M.; Graham G. J.; Horuk R.; Sparre-Ulrich A. H.; Locati M.; Luster A. D.; Mantovani A.; Matsushima K.; Murphy P. M.; Nibbs R.; Nomiyama H.; Power C. A.; Proudfoot A. E.; Rosenkilde M. M.; Rot A.; Sozzani S.; Thelen M.; Yoshie O.; Zlotnik A. (2014) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. [corrected]. LXXXIX. Update on the extended family of chemokine receptors and introducing a new nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 66 (1), 1–79. 10.1124/pr.113.007724. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burns J. M.; Summers B. C.; Wang Y.; Melikian A.; Berahovich R.; Miao Z.; Penfold M. E.; Sunshine M. J.; Littman D. R.; Kuo C. J.; Wei K.; McMaster B. E.; Wright K.; Howard M. C.; Schall T. J. (2006) A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J. Exp. Med. 203 (9), 2201–13. 10.1084/jem.20052144. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
