Design, Synthesis, Pharmacokinetics, and Biodistribution of a Series of Bone-Targeting EP4 Receptor Agonist Prodrugs for Treatment of Osteoporosis and Other Bone Conditions
- PMID: 33860210
- PMCID: PMC8033786
- DOI: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00027
Design, Synthesis, Pharmacokinetics, and Biodistribution of a Series of Bone-Targeting EP4 Receptor Agonist Prodrugs for Treatment of Osteoporosis and Other Bone Conditions
Abstract
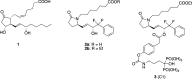
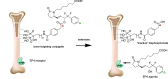
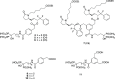
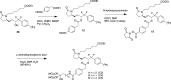
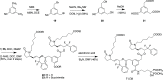
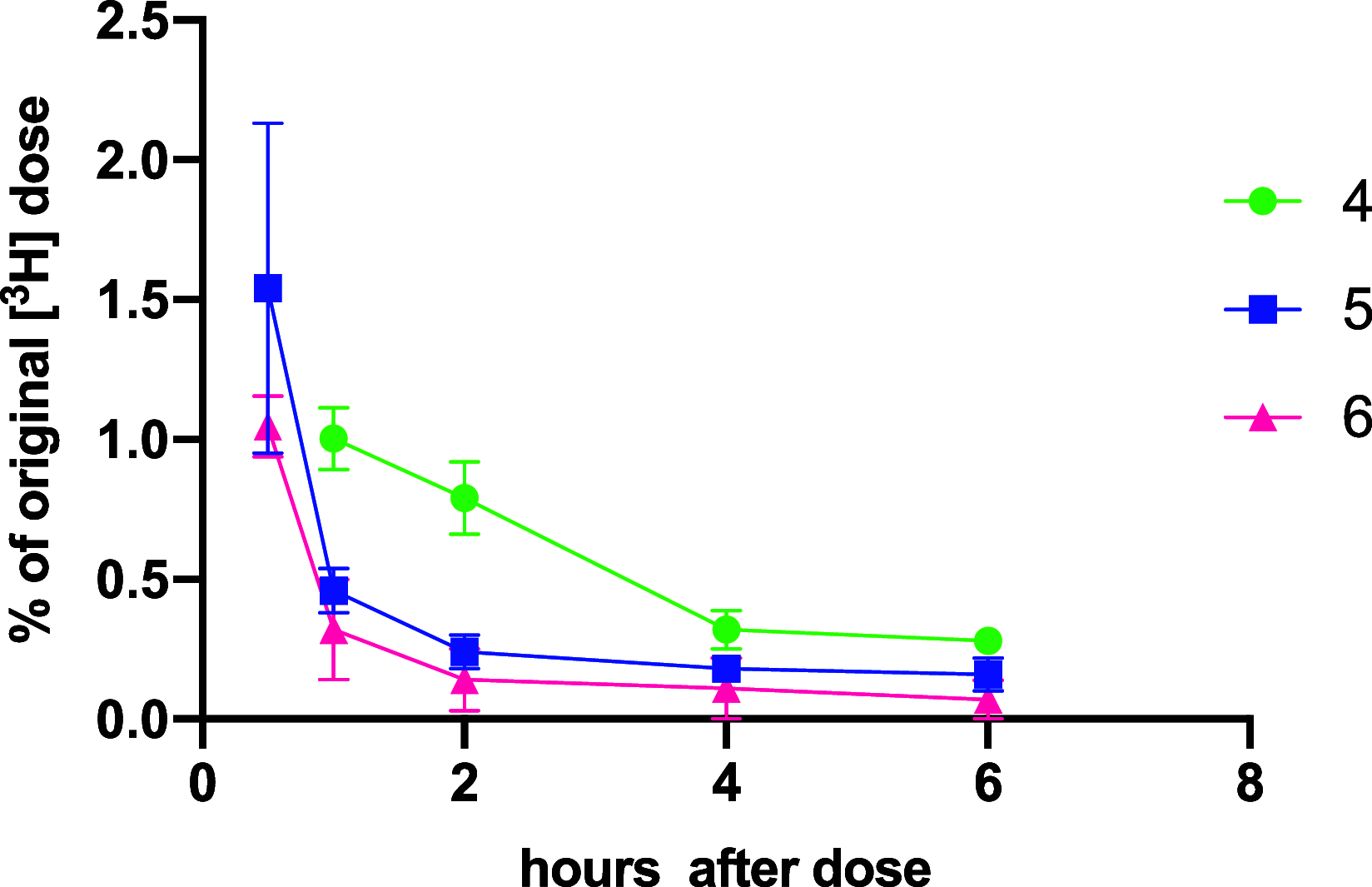
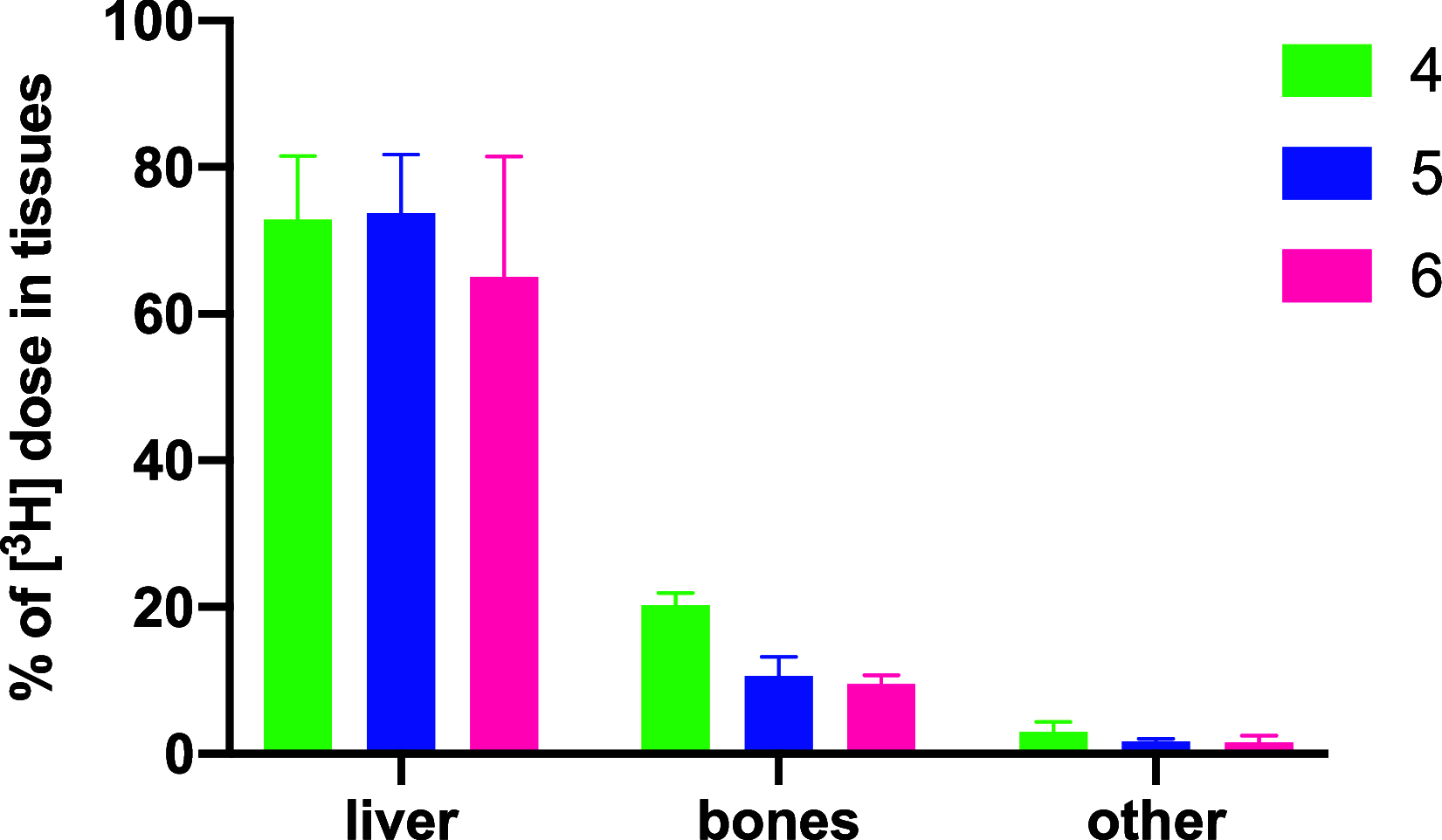
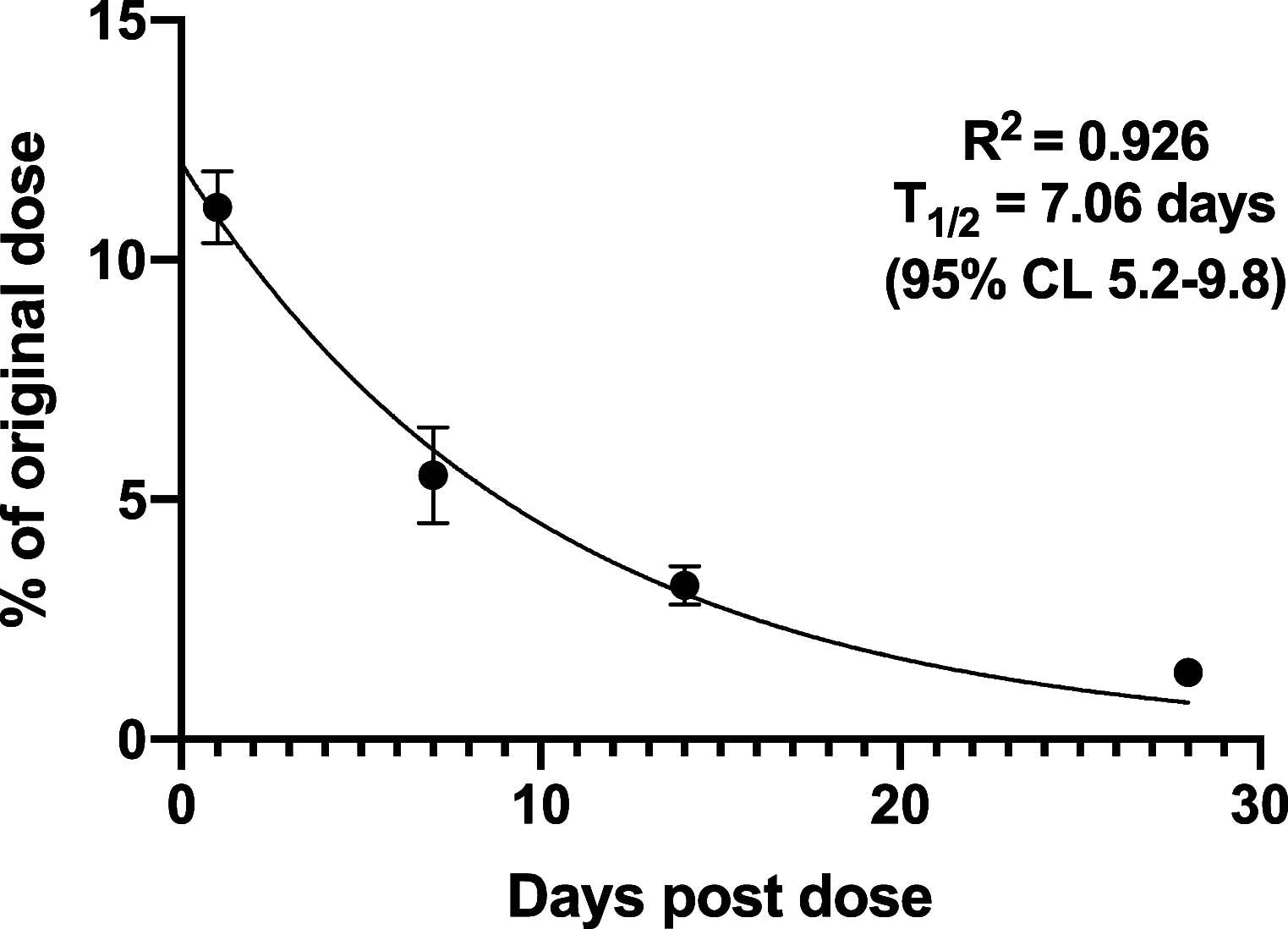
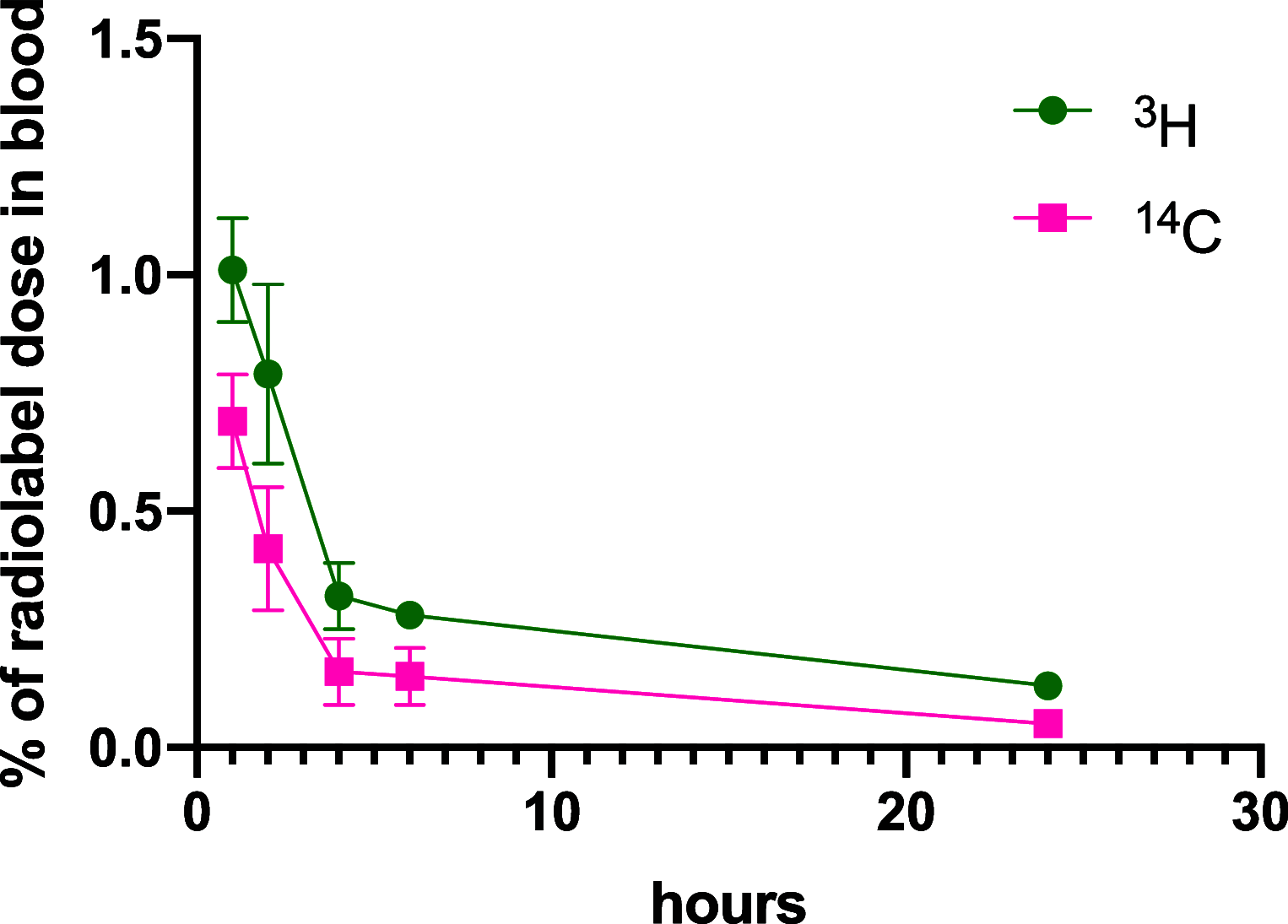
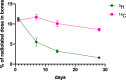
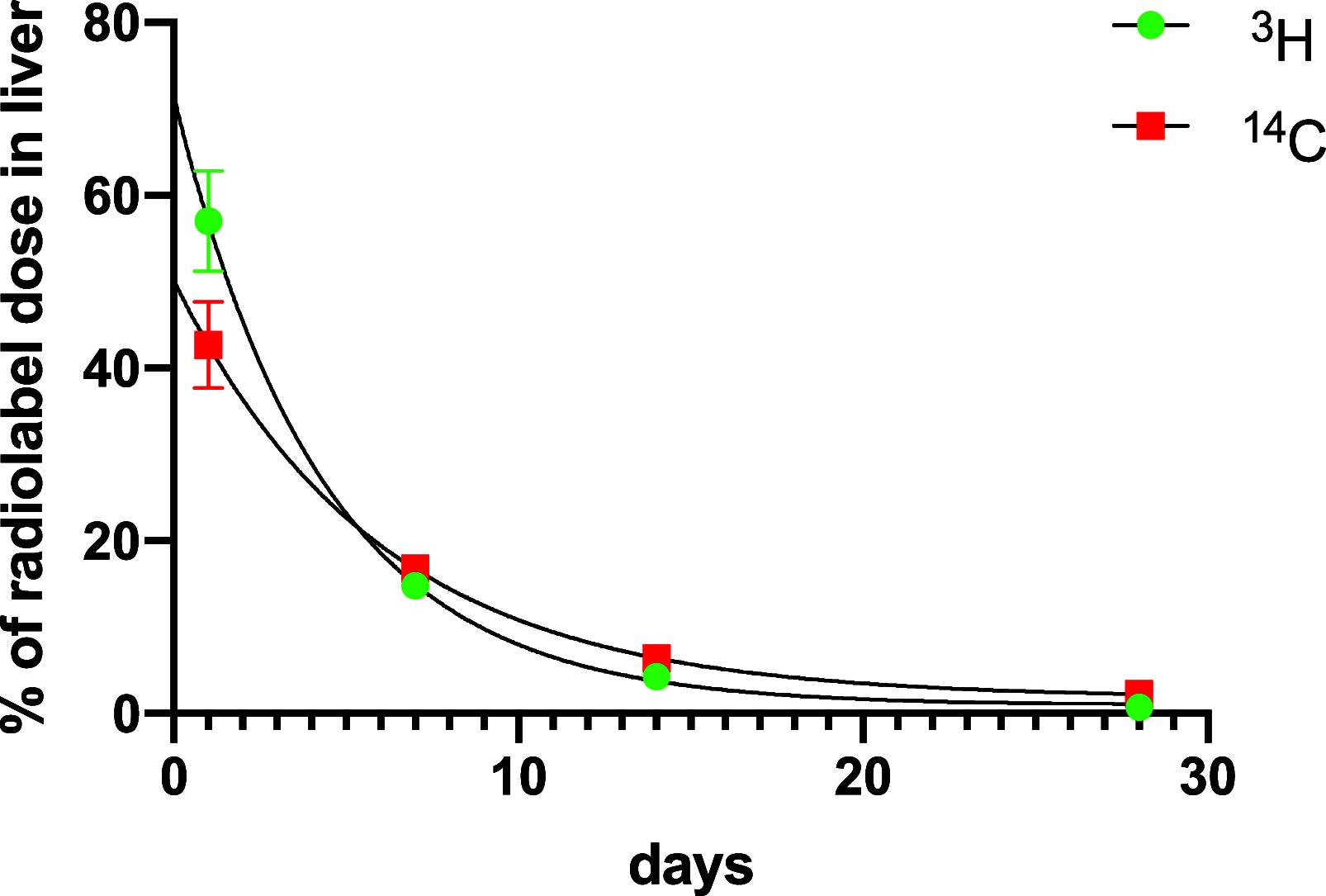
A series of bone-targeting EP4 receptor agonist conjugate prodrugs were prepared wherein a potent EP4 receptor agonist was bound to a biologically inactive, bisphosphonate-based bone-targeting moiety. Singly and doubly radiolabeled conjugates were synthesized and were shown to be stable in blood, to be rapidly eliminated from the bloodstream, and to be effectively taken up into bone in vivo after intravenous dosing. From these preliminary studies a preferred conjugate 4 (also known as C3 and Mes-1007) was selected for follow up biodistribution and elimination studies. Doubly radiolabeled conjugate 4 was found to partition largely to the liver and bones, and both labels were eliminated from liver at the same rate indicating the conjugate was eliminated intact. Quantification of the labels in bones indicated that free EP4 agonist (EP4a)(2a) was released from bone-bound 4 with a half-time of about 7 days. When dosed orally, radiolabeled 4 was not absorbed and passed through the gastrointestinal tract essentially unchanged, and only traces of radiolabeled 4 were found in the liver, blood, or bones. 4 was found to bind rapidly and completely to powdered bone mineral or to various forms of calcium phosphate, forming a stable matrix suitable for implant and that could made into powders or solid forms and be sterilized without decomposition or release of 4. Basic hydrolysis released free EP4 agonist 2a quantitatively from the material.
© 2021 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): R.Y. and M.G. hold equity positions in Mesentech, Inc., which has a license to right to the compounds described in this publication. R.Y., G.C., and M.T. are co-inventors on patents (WO2016IB53482 (June 12, 2016), published December 15, 2016, as WO16199111 A1; US-2018-0170951-A1 (June 21, 2018); US Patent No. 10,400,000 (September 3, 2019)) covering the intellectual property derived from this work.
Figures

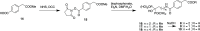
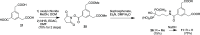
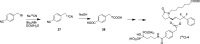
Similar articles
-
Design and synthesis of novel bone-targeting dual-action pro-drugs for the treatment and reversal of osteoporosis.Bioorg Med Chem. 2012 Mar 15;20(6):2131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.01.024. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22341574
-
Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacokinetics of a Bone-Targeting Dual-Action Prodrug for the Treatment of Osteoporosis.J Med Chem. 2017 Aug 24;60(16):7012-7028. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00951. Epub 2017 Aug 10. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28699744
-
Targeting therapeutics to bone by conjugation with bisphosphonates.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;40:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2018.03.010. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29626715 Review.
-
Novel EP4 receptor agonist-bisphosphonate conjugate drug (C1) promotes bone formation and improves vertebral mechanical properties in the ovariectomized rat model of postmenopausal bone loss.J Bone Miner Res. 2015 Apr;30(4):670-80. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2382. J Bone Miner Res. 2015. PMID: 25284325
-
[Role of EP4 receptor in bone resorption induced by PGE].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Apr;117(4):293-7. doi: 10.1254/fpj.117.293. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11338379 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Hydroxy- and Amino-Phosphonates and -Bisphosphonates: Synthetic Methods and Their Biological Applications.Front Chem. 2022 Jun 1;10:890696. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.890696. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35721002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Machwate M.; Harada S.; Leu C. T.; Seedor G.; Labelle M.; Gallant M.; Hutchins S.; Lachance N.; Sawyer N.; Slipetz D.; Metters K. M.; Rodan S. B.; Young R.; Rodan G. A. (2001) Prostaglandin receptor EP(4) mediates the bone anabolic effects of PGE(2). Mol. Pharmacol. 60, 36–41. 10.1124/mol.60.1.36. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Billot X., Young R. N., and Han Y. (2003) 1,5-Distributed pyrrolid-2-one derivatives for use as ep4 receptor agonists in the treatment of eye diseases such as glaucoma, WO2003103772A1.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
