First morphological and molecular identification of third-stage larvae of Anisakis typica (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from marine fishes in Vietnamese water
- PMID: 33860256
- PMCID: PMC8039996
- DOI: 10.21307/jofnem-2021-010
First morphological and molecular identification of third-stage larvae of Anisakis typica (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from marine fishes in Vietnamese water
Abstract
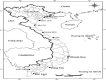
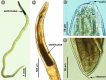
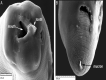
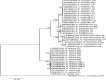
Anisakid nematodes are parasites of cetaceans, their larval stages live in marine fishes. The third-stage larvae of some Anisakis species are also the etiological agents of human anisakiasis caused by consumption of raw or undercooked infected fish. Thus, identification of Anisakis larvae at the species level is crucial for their ecology and epidemiology. In Vietnam, although Anisakis larvae have been reported, they have not been identified to the species level. The aim of this study was, therefore, to identify third-stage larvae of Anisakis collected from marine fishes in Vietnamese water, based on morphological characteristics and molecular analysis. All Anisakis larvae found in this study were morphologically similar to each other and identical to Anisakis typica. In addition, molecular analysis based on ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 sequences confirmed them as A. typica. Vietnamese A. typica population was genetically close to those from Asian countries and Australia. The third-stage larvae of A. typica were collected from eight fish species from three localities in the South of Vietnam. Among them, seven were recorded as new intermediate hosts of A. typica. This is the first identification of A. typica larvae in Vietnamese water with records of new fish hosts.
Keywords: Anisakid larvae; Intermediate fish host; Molecular analyzes; Morphology; Vietnam.
© 2021 Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Morphological and molecular identification of third-stage larvae of Anisakis typica (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from Red Sea coral trout, Plectropomus areolatus.Parasitol Res. 2023 Mar;122(3):705-715. doi: 10.1007/s00436-022-07776-1. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 36650313 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification of Anisakis and Hysterothylacium larvae in marine fishes from the East China Sea and the Pacific coast of central Japan.Int J Food Microbiol. 2015 Apr 16;199:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25617845
-
Genetic differentiation of Anisakis species (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in marine fish Priacanthus tayenus from Gulf of Thailand.Trop Biomed. 2018 Sep 1;35(3):669-677. Trop Biomed. 2018. PMID: 33601754
-
The occurrence of Anisakis spp. in Australian waters: past, present, and future trends.Parasitol Res. 2021 Sep;120(9):3007-3033. doi: 10.1007/s00436-021-07243-3. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Parasitol Res. 2021. PMID: 34341859 Review.
-
Anisakiasis and Anisakis: An underdiagnosed emerging disease and its main etiological agents.Res Vet Sci. 2020 Oct;132:535-545. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.08.003. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Res Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32828066 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Ascaridoid Parasites of Philippine Decapterus Species.J Nematol. 2022 Aug 14;54(1):20220030. doi: 10.2478/jofnem-2022-0030. eCollection 2022 Feb. J Nematol. 2022. PMID: 36060477 Free PMC article.
-
Ascaridoid nematodes infecting commercially important marine fish and squid species from Bangladesh waters in the Bay of Bengal.Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2022 Apr 25;27:e00157. doi: 10.1016/j.fawpar.2022.e00157. eCollection 2022 Jun. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35518125 Free PMC article.
-
Single-worm long-read sequencing reveals genome diversity in free-living nematodes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Aug 25;51(15):8035-8047. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad647. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37526286 Free PMC article.
-
Invasion dynamics and ecological impacts of Anisakis typica in commercial fish from the Western Pacific Ocean.Vet World. 2025 May;18(5):1365-1376. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2025.1365-1376. Epub 2025 May 31. Vet World. 2025. PMID: 40584111 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and molecular identification of third-stage larvae of Anisakis typica (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from Red Sea coral trout, Plectropomus areolatus.Parasitol Res. 2023 Mar;122(3):705-715. doi: 10.1007/s00436-022-07776-1. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 36650313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arthur, J. R. and Te, B. Q.. 2006. Checklist of the parasites of fishes of Viet Nam FAO, Rome.
-
- Audicana, M. T., Ansotegui, I. J., de Corres, L. F. and Kennedy, M. W.. 2002. Anisakis simplex: dangerous – dead and alive?. Trends in Parasitology 18:20–25. - PubMed
-
- Berland, B. 1961. Nematodes from some Norwegian marine fishes. Sarsia 2:1–50.
-
- Chen, H. Y. and Shih, H. H.. 2015. Occurrence and prevalence of fish-borne Anisakis larvae in the spotted mackerel Scomber australasicus from Taiwanese waters. Acta Tropica 145:61–67. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
