Targeted sequencing and integrative analysis to prioritize candidate genes in neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 33860439
- PMCID: PMC8280036
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-021-02377-y
Targeted sequencing and integrative analysis to prioritize candidate genes in neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
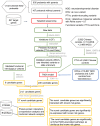
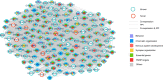
Neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) are a group of diseases characterized by high heterogeneity and frequently co-occurring symptoms. The mutational spectrum in patients with NDDs is largely incomplete. Here, we sequenced 547 genes from 1102 patients with NDDs and validated 1271 potential functional variants, including 108 de novo variants (DNVs) in 78 autosomal genes and seven inherited hemizygous variants in six X chromosomal genes. Notably, 36 of these 78 genes are the first to be reported in Chinese patients with NDDs. By integrating our genetic data with public data, we prioritized 212 NDD candidate genes with FDR < 0.1, including 17 novel genes. The novel candidate genes interacted or were co-expressed with known candidate genes, forming a functional network involved in known pathways. We highlighted MSL2, which carried two de novo protein-truncating variants (p.L192Vfs*3 and p.S486Ifs*11) and was frequently connected with known candidate genes. This study provides the mutational spectrum of NDDs in China and prioritizes 212 NDD candidate genes for further functional validation and genetic counseling.
Keywords: Candidate genes; De novo variants; Neurodevelopmental disorders; Targeted sequencing.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted sequencing and integrative analysis of 3,195 Chinese patients with neurodevelopmental disorders prioritized 26 novel candidate genes.J Genet Genomics. 2021 Apr 20;48(4):312-323. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.03.002. Epub 2021 Apr 1. J Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33994118
-
Rare deleterious mutations of HNRNP genes result in shared neurodevelopmental disorders.Genome Med. 2021 Apr 19;13(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00870-6. Genome Med. 2021. PMID: 33874999 Free PMC article.
-
De novo mutation of cancer-related genes associates with particular neurodevelopmental disorders.J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Dec;98(12):1701-1712. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01991-y. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020. PMID: 33047154
-
Genetic Counseling in Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020 Apr 1;10(4):a036533. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036533. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020. PMID: 31501260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding the genetic and phenotypic relevance of KCNB1 variants in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies: 27 new patients and overview of the literature.Hum Mutat. 2020 Jan;41(1):69-80. doi: 10.1002/humu.23915. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Hum Mutat. 2020. PMID: 31513310 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel protein-truncating variants of a chromatin-modifying gene MSL2 in syndromic neurodevelopmental disorders.Eur J Hum Genet. 2024 Jul;32(7):879-883. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01576-0. Epub 2024 May 3. Eur J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38702431 Free PMC article.
-
MSL2 variants lead to a neurodevelopmental syndrome with lack of coordination, epilepsy, specific dysmorphisms, and a distinct episignature.Am J Hum Genet. 2024 Jul 11;111(7):1330-1351. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.05.001. Epub 2024 May 29. Am J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38815585 Free PMC article.
-
Truncated SPAG9 as a novel candidate gene for a new syndrome: Coarse facial features, albinism, cataract and developmental delay (CACD syndrome).Genet Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 20;48(1):e20240094. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2024-0094. eCollection 2025. Genet Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39846792 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis prioritised oxytocin-related biomarkers associated with the aetiology of autism spectrum disorder.EBioMedicine. 2022 Jul;81:104091. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104091. Epub 2022 Jun 2. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35665681 Free PMC article.
-
A rigorous in silico genomic interrogation at 1p13.3 reveals 16 autosomal dominant candidate genes in syndromic neurodevelopmental disorders.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 6;15:979061. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.979061. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36277487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stessman HAF, Xiong B, Coe BP, Wang T, Hoekzema K, Fenckova M, Kvarnung M, Gerdts J, Trinh S, Cosemans N, Vives L, Lin J, Turner TN, Santen G, Ruivenkamp C, Kriek M, van Haeringen A, Aten E, Friend K, Liebelt J, Barnett C, Haan E, Shaw M, Gecz J, Anderlid BM, Nordgren A, Lindstrand A, Schwartz C, Kooy RF, Vandeweyer G, Helsmoortel C, Romano C, Alberti A, Vinci M, Avola E, Giusto S, Courchesne E, Pramparo T, Pierce K, Nalabolu S, Amaral DG, Scheffer IE, Delatycki MB, Lockhart PJ, Hormozdiari F, Harich B, Castells-Nobau A, Xia K, Peeters H, Nordenskjöld M, Schenck A, Bernier RA, Eichler EE. Targeted sequencing identifies 91 neurodevelopmental-disorder risk genes with autism and developmental-disability biases. Nat Genet. 2017;49(4):515–526. doi: 10.1038/ng.3792. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

