Liver macrophages and inflammation in physiology and physiopathology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 33860630
- PMCID: PMC9290065
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.15877
Liver macrophages and inflammation in physiology and physiopathology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
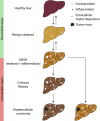
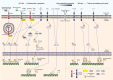
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome, being a common comorbidity of type 2 diabetes and with important links to inflammation and insulin resistance. NAFLD represents a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from steatosis in the form of ectopic lipid storage, to inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Macrophages that populate the liver play important roles in maintaining liver homeostasis under normal physiology and in promoting inflammation and mediating fibrosis in the progression of NAFLD toward to NASH. Liver macrophages are a heterogenous group of innate immune cells, originating from the yolk sac or from circulating monocytes, that are required to maintain immune tolerance while being exposed portal and pancreatic blood flow rich in nutrients and hormones. Yet, liver macrophages retain a limited capacity to raise the alarm in response to danger signals. We now know that macrophages in the liver play both inflammatory and noninflammatory roles throughout the progression of NAFLD. Macrophage responses are mediated first at the level of cell surface receptors that integrate environmental stimuli, signals are transduced through multiple levels of regulation in the cell, and specific transcriptional programmes dictate effector functions. These effector functions play paramount roles in determining the course of disease in NAFLD and even more so in the progression towards NASH. The current review covers recent reports in the physiological and pathophysiological roles of liver macrophages in NAFLD. We emphasise the responses of liver macrophages to insulin resistance and the transcriptional machinery that dictates liver macrophage function.
Keywords: NAFLD; NASH; inflammation; liver; macrophages.
© 2021 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM & Ahmed A (2015) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 148, 547–555. - PubMed
-
- Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M, George J & Bugianesi E (2018) Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15, 11–20. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, Qiu Y, Burns L, Afendy A & Nader F (2019) The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Hepatol 71, 793–801. - PubMed
-
- Gehrke N & Schattenberg JM (2020) Metabolic inflammation‐a role for hepatic inflammatory pathways as drivers of comorbidities in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? Gastroenterology 158, 1929–1947.e6. - PubMed
-
- Sheka AC, Adeyi O, Thompson J, Hameed B, Crawford PA & Ikramuddin S (2020) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a review. JAMA 323, 1175–1183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

